Vitamin D Receptor (PTR2542) Mouse mAb
- Catalog No.:YM4683
- Applications:WB;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human
- Target:
- Vitamin D Receptor
- Fields:
- >>Parathyroid hormone synthesis, secretion and action;>>Endocrine and other factor-regulated calcium reabsorption;>>Mineral absorption;>>Tuberculosis;>>Chemical carcinogenesis - receptor activation
- Gene Name:
- VDR NR1I1
- Protein Name:
- Vitamin D3 receptor (VDR) (1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 receptor) (Nuclear receptor subfamily 1 group I member 1)
- Human Gene Id:
- 7421
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P11473
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 22337
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P48281
- Rat Gene Id:
- 24873
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- P13053
- Immunogen:
- Synthesized peptide derived from human Vitamin D Receptor AA range: 150-250
- Specificity:
- This antibody detects endogenous levels of Vitamin D Receptor at Human
- Formulation:
- PBS, pH7.4, 50% glycerol, 0.03%Proclin 300
- Source:
- Mouse,monoclonal:IgG1,Kappa
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500-2000 ELISA 1:5000-20000
- Purification:
- Protein G
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- Vitamin D3 receptor (VDR) (1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 receptor) (Nuclear receptor subfamily 1 group I member 1)
- Observed Band(KD):
- 48kDa
- Background:
- vitamin D (1,25- dihydroxyvitamin D3) receptor(VDR) Homo sapiens This gene encodes the nuclear hormone receptor for vitamin D3. This receptor also functions as a receptor for the secondary bile acid lithocholic acid. The receptor belongs to the family of trans-acting transcriptional regulatory factors and shows sequence similarity to the steroid and thyroid hormone receptors. Downstream targets of this nuclear hormone receptor are principally involved in mineral metabolism though the receptor regulates a variety of other metabolic pathways, such as those involved in the immune response and cancer. Mutations in this gene are associated with type II vitamin D-resistant rickets. A single nucleotide polymorphism in the initiation codon results in an alternate translation start site three codons downstream. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different proteins. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2011],
- Function:
- caution:It is uncertain whether Met-1 or Met-4 is the initiator.,disease:Defects in VDR are the cause of type IIA rickets [MIM:277440]; also known as hypocalcemic vitamin D-resistant rickets (HVDRR). HVDRR is most frequently an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by severe rickets, hypocalcemia and secondary hyperparathyroidism.,domain:Composed of three domains: a modulating N-terminal domain, a DNA-binding domain and a C-terminal steroid-binding domain.,function:Nuclear hormone receptor. Transcription factor that mediates the action of vitamin D3 by controlling the expression of hormone sensitive genes. Regulates transcription of hormone sensitive genes via its association with the WINAC complex, a chromatin-remodeling complex. Recruited to promoters via its interaction with the WINAC complex subunit BAZ1B/WSTF, which mediates the interaction with acetylated histones, an essentia
- Subcellular Location:
- Nucleus . Cytoplasm . Localizes mainly to the nucleus (PubMed:28698609, PubMed:12145331). Localization to the nucleus is enhanced by vitamin D3. .
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
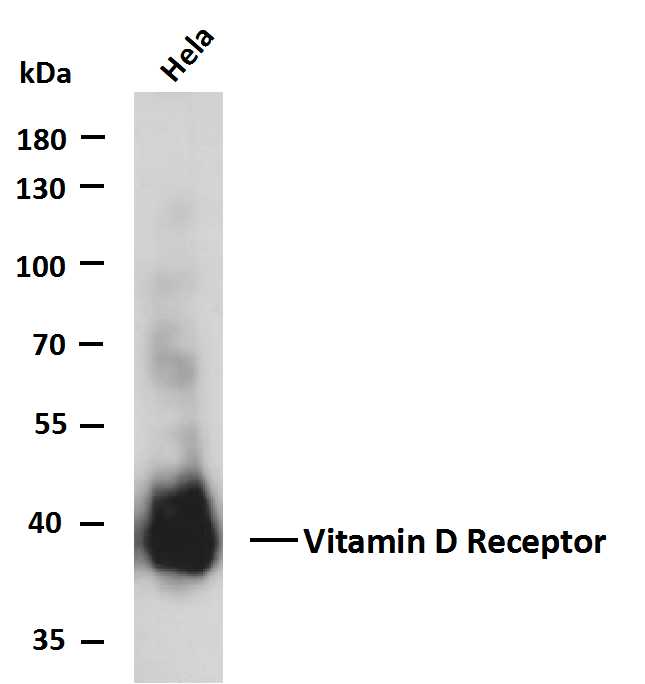
- Whole cell lysates of Hela were separated by 10% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with anti-Vitamin D Receptor(PTR2542) antibody. The HRP-conjugated Goat anti-Mouse IgG(H + L) antibody was used to detect the antibody. Lane 1: Hela Predicted band size: 48kDa Observed band size: 37kDa