α-tubulin Monoclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YM3115
- Applications:WB
- Reactivity:Zebrafish
- Target:
- Tubulin α
- Fields:
- >>Phagosome;>>Gap junction;>>Alzheimer disease;>>Parkinson disease;>>Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis;>>Huntington disease;>>Prion disease;>>Pathways of neurodegeneration - multiple diseases;>>Pathogenic Escherichia coli infection;>>Salmonella infection
- Gene Name:
- TUBA1A
- Protein Name:
- Tubulin alpha-1A chain
- Human Gene Id:
- 7846/10376
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- Q71U36/P68363
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 22142/22143
- Rat Gene Id:
- 64158/500929
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- P68370/Q6P9V9
- Immunogen:
- Recombinant Protein of Tubulin alpha-1A chain
- Specificity:
- The antibody detects Zebrafish endogenous α-tubulin protein.
- Formulation:
- PBS, pH 7.4, containing 0.5%BSA, 0.02% sodium azide as Preservative and 50% Glycerol.
- Source:
- Monoclonal, Mouse
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500-10000
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from mouse ascites by affinity-chromatography using specific immunogen.
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- TUBA1A
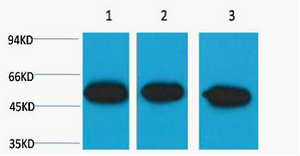
- Observed Band(KD):
- 52kD
- Background:
- Microtubules of the eukaryotic cytoskeleton perform essential and diverse functions and are composed of a heterodimer of alpha and beta tubulins. The genes encoding these microtubule constituents belong to the tubulin superfamily, which is composed of six distinct families. Genes from the alpha, beta and gamma tubulin families are found in all eukaryotes. The alpha and beta tubulins represent the major components of microtubules, while gamma tubulin plays a critical role in the nucleation of microtubule assembly. There are multiple alpha and beta tubulin genes, which are highly conserved among species. This gene encodes alpha tubulin and is highly similar to the mouse and rat Tuba1 genes. Northern blotting studies have shown that the gene expression is predominantly found in morphologically differentiated neurologic cells. This gene is one of three alpha-tubulin genes in a cluster on chromosome 12q.
- Function:
- disease:Defects in TUBA1A are the cause of lissencephaly type 3 (LIS3) [MIM:611603]. LIS is characterized by a smooth brain surface due to the absence (agyria) or reduction (pachygyria) of surface convolutions. It is often associated with psychomotor retardation and seizures. LIS3 features include agyria or pachygyria or laminar heterotopia, severe mental retardation, motor delay, variable presence of seizures, and abnormalities of corpus callosum, hippocampus, cerebellar vermis and brainstem.,function:Tubulin is the major constituent of microtubules. It binds two moles of GTP, one at an exchangeable site on the beta chain and one at a non-exchangeable site on the alpha-chain.,PTM:Undergoes a tyrosination/detyrosination cycle, the cyclic removal and re-addition of a C-terminal tyrosine residue by the enzymes tubulin tyrosine carboxypeptidase (TTCP) and tubulin tyrosine ligase (TTL), resp
- Subcellular Location:
- Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton.
- Expression:
- Expressed at a high level in fetal brain.
Lrwd1 impacts cell proliferation and the silencing of repetitive DNA elements. GENESIS2022 May;60(4-5):e23475. Mouse 1:10000 MEFs
FGF18–FGFR2 signaling triggers the activation of c-Jun–YAP1 axis to promote carcinogenesis in a subgroup of gastric cancer patients and indicates translational potential. ONCOGENE 2020 Sep 15 WB Human MGC-803 cell,AGS cell
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
.jpg)
- Zhang, J., Wong, C.C., Leung, K.T. et al. FGF18–FGFR2 signaling triggers the activation of c-Jun–YAP1 axis to promote carcinogenesis in a subgroup of gastric cancer patients and indicates translational potential. Oncogene 39, 6647–6663 (2020).

- Western blot analysis of Zebrafish skeletal muscle, (Zebrafish Specific) diluted at 1:5000.