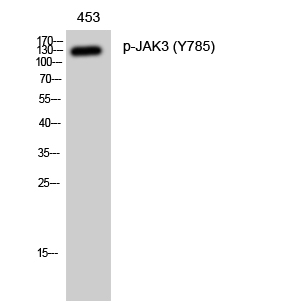
Phospho JAK3 (Y785) Cell-Based Colorimetric ELISA Kit
- Catalog No.:KA1501C
- Applications:ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Gene Name:
- JAK3
- Human Gene Id:
- 3718
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P52333
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- Q62137
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- Q63272
- Storage Stability:
- 2-8°C/6 months
- Other Name:
- Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK3 (EC 2.7.10.2) (Janus kinase 3) (JAK-3) (Leukocyte janus kinase) (L-JAK)
- Detection Method:
- Colorimetric
- Background:
- catalytic activity:ATP + a [protein]-L-tyrosine = ADP + a [protein]-L-tyrosine phosphate.,disease:Defects in JAK3 are a cause of severe combined immunodeficiency autosomal recessive T-cell-negative/B-cell-positive/NK-cell-negative (T(-)B(+)NK(-)SCID) [MIM:600802]. SCID refers to a genetically and clinically heterogeneous group of rare congenital disorders characterized by impairment of both humoral and cell-mediated immunity, leukopenia, and low or absent antibody levels. Patients with SCID present in infancy with recurrent, persistent infections by opportunistic organisms. The common characteristic of all types of SCID is absence of T-cell-mediated cellular immunity due to a defect in T-cell development.,domain:Possesses two phosphotransferase domains. The second one probably contains the catalytic domain (By similarity), while the presence of slight differences suggest a different role for domain 1.,function:Tyrosine kinase of the non-receptor type, involved in the interleukin-2 and interleukin-4 signaling pathway. Phosphorylates STAT6, IRS1, IRS2 and PI3K.,online information:JAK3 mutation db,PTM:Tyrosine phosphorylated in response to IL-2 and IL-4.,similarity:Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. Tyr protein kinase family. JAK subfamily.,similarity:Contains 1 FERM domain.,similarity:Contains 1 protein kinase domain.,similarity:Contains 1 SH2 domain.,subcellular location:Wholly intracellular, possibly membrane associated.,subunit:Interacts with STAM2 and MYO18A (By similarity). Interacts with SHB.,tissue specificity:In NK cells and an NK-like cell line but not in resting T-cells or in other tissues. The S-form is more commonly seen in hematopoietic lines, whereas the B- and M-forms are detected in cells both of hematopoietic and epithelial origins.,
- Function:
- regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent, regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter, protein amino acid phosphorylation, phosphorus metabolic process, phosphate metabolic process, cell surface receptor linked signal transduction, enzyme linked receptor protein signaling pathway, intracellular signaling cascade, protein kinase cascade, positive regulation of biosynthetic process, positive regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process,positive regulation of macromolecule metabolic process, positive regulation of gene expression, phosphorylation,peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation, peptidyl-tyrosine modification, cytokine-mediated signaling pathway, positive regulation of cellular biosynthetic process, regulation of transcription, positive regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent, positive regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic pro
- Subcellular Location:
- Endomembrane system ; Peripheral membrane protein . Cytoplasm .
- Expression:
- In NK cells and an NK-like cell line but not in resting T-cells or in other tissues. The S-form is more commonly seen in hematopoietic lines, whereas the B-form is detected in cells both of hematopoietic and epithelial origins.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs