Ephrin-A5 Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YC0079
- Applications:WB;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Target:
- Ephrin-A5
- Fields:
- >>MAPK signaling pathway;>>Ras signaling pathway;>>Rap1 signaling pathway;>>PI3K-Akt signaling pathway;>>Axon guidance;>>MicroRNAs in cancer
- Gene Name:
- EFNA5
- Protein Name:
- Ephrin-A5
- Human Gene Id:
- 1946
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P52803
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 13640
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- O08543
- Rat Gene Id:
- 116683
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- P97605
- Immunogen:
- Synthesized peptide derived from Ephrin-A5 . at AA range: 130-210
- Specificity:
- Ephrin-A5 Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of Ephrin-A5 protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. ELISA: 1:40000. Not yet tested in other applications.
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- EFNA5;EPLG7;LERK7;Ephrin-A5;AL-1;EPH-related receptor tyrosine kinase ligand 7;LERK-7
- Observed Band(KD):
- 26kD
- Background:
- Ephrin-A5, a member of the ephrin gene family, prevents axon bundling in cocultures of cortical neurons with astrocytes, a model of late stage nervous system development and differentiation. The EPH and EPH-related receptors comprise the largest subfamily of receptor protein-tyrosine kinases and have been implicated in mediating developmental events, particularly in the nervous system. EPH receptors typically have a single kinase domain and an extracellular region containing a Cys-rich domain and 2 fibronectin type III repeats. The ephrin ligands and receptors have been named by the Eph Nomenclature Committee (1997). Based on their structures and sequence relationships, ephrins are divided into the ephrin-A (EFNA) class, which are anchored to the membrane by a glycosylphosphatidylinositol linkage, and the ephrin-B (EFNB) class, which are transmembrane proteins. The Eph family of receptors are similarly divi
- Function:
- function:May function actively to stimulate axon fasciculation. Induces compartmentalized signaling within a caveolae-like membrane microdomain when bound to the extracellular domain of its cognate receptor. This signaling event requires the activity of the Fyn tyrosine kinase.,similarity:Belongs to the ephrin family.,subcellular location:Compartmentalized in discrete caveolae-like membrane microdomains.,subunit:Binds to EPHB2 (By similarity). Binds to the receptor tyrosine kinases EPHA2, EPHA3 and EPHB1.,
- Subcellular Location:
- Cell membrane ; Lipid-anchor, GPI-anchor . Membrane, caveola ; Lipid-anchor, GPI-anchor . Compartmentalized in discrete caveolae-like membrane microdomains.
- Expression:
- Brain,
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
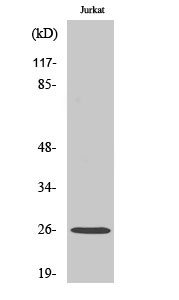
- Western Blot analysis of various cells using Ephrin-A5 Polyclonal Antibody



