A-FABP Monoclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YM0013
- Applications:WB;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human
- Target:
- A-FABP
- Fields:
- >>PPAR signaling pathway;>>Regulation of lipolysis in adipocytes
- Gene Name:
- FABP4
- Protein Name:
- Fatty acid-binding protein, adipocyte
- Human Gene Id:
- 2167
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P15090
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P04117
- Immunogen:
- Purified recombinant fragment of A-FABP (aa61-121) expressed in E. Coli.
- Specificity:
- A-FABP Monoclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of A-FABP protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Monoclonal, Mouse
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. ELISA: 1:10000. Not yet tested in other applications.
- Purification:
- Affinity purification
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- FABP4;Fatty acid-binding protein; adipocyte;Adipocyte lipid-binding protein;ALBP;Adipocyte-type fatty acid-binding protein;A-FABP;AFABP;Fatty acid-binding protein 4
- Molecular Weight(Da):
- 15kD
- References:
- 1. J Biol Chem. 2004 Dec 10;279(50):52399-405.
2. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2005 Apr;4(4):570-81.
- Background:
- FABP4 encodes the fatty acid binding protein found in adipocytes. Fatty acid binding proteins are a family of small, highly conserved, cytoplasmic proteins that bind long-chain fatty acids and other hydrophobic ligands. It is thought that FABPs roles include fatty acid uptake, transport, and metabolism. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],
- Function:
- domain:Forms a beta-barrel structure that accommodates hydrophobic ligands in its interior.,function:Lipid transport protein in adipocytes. Binds both long chain fatty acids and retinoic acid. Delivers long-chain fatty acids and retinoic acid to their cognate receptors in the nucleus.,similarity:Belongs to the calycin superfamily. Fatty-acid binding protein (FABP) family.,subcellular location:Depending on the nature of the ligand, a conformation change exposes a nuclear localization motif and the protein is transported into the nucleus. Subject to constitutive nuclear export.,subunit:Homodimer. Interacts with PPARG (By similarity). Monomer.,
- Subcellular Location:
- Cytoplasm . Nucleus . Depending on the nature of the ligand, a conformation change exposes a nuclear localization motif and the protein is transported into the nucleus. Subject to constitutive nuclear export. .
- Expression:
- Urinary bladder,
A Novel in Duck Myoblasts: The Transcription Factor Retinoid X Receptor Alpha (RXRA) Inhibits Lipid Accumulation by Promoting CD36 Expression INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MOLECULAR SCIENCES Zhaoyu Geng WB Duck myoblasts (CS2 cells)
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
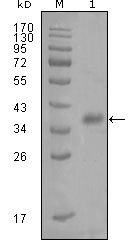
- Western Blot analysis using A-FABP Monoclonal Antibody against truncated Trx-FABP4 recombinant protein (1).
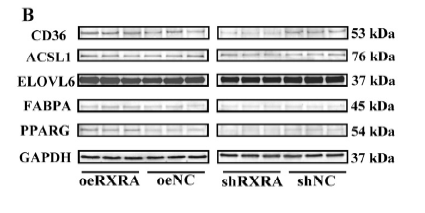
- A Novel in Duck Myoblasts: The Transcription Factor Retinoid X Receptor Alpha (RXRA) Inhibits Lipid Accumulation by Promoting CD36 Expression INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MOLECULAR SCIENCES Zhaoyu Geng WB,IF Duck myoblasts (CS2 cells)



