ALB Monoclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YM0021
- Applications:WB;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human
- Target:
- Albumin
- Fields:
- >>Thyroid hormone synthesis
- Gene Name:
- ALB
- Protein Name:
- Serum albumin
- Human Gene Id:
- 213
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P02768
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P07724
- Immunogen:
- Human sera albumin.
- Specificity:
- ALB Monoclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of ALB protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Monoclonal, Mouse
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. ELISA: 1:10000. Not yet tested in other applications.
- Purification:
- Affinity purification
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- ALB;GIG20;GIG42;Serum albumin
- Molecular Weight(Da):
- 69kD
- References:
- 1. Proteins. 2006 Aug 1;64(2):355-62.
2. FEBS Lett. 2007 Jul 10;581(17):3178-82.
- Background:
- This gene encodes the most abundant protein in human blood. This protein functions in the regulation of blood plasma colloid osmotic pressure and acts as a carrier protein for a wide range of endogenous molecules including hormones, fatty acids, and metabolites, as well as exogenous drugs. Additionally, this protein exhibits an esterase-like activity with broad substrate specificity. The encoded preproprotein is proteolytically processed to generate the mature protein. A peptide derived from this protein, EPI-X4, is an endogenous inhibitor of the CXCR4 chemokine receptor. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2016],
- Function:
- caution:A peptide arising from positions 166 to 174 was originally (PubMed:3087352 and PubMed:2437111) termed neurotensin-related peptide (NRP) or kinetensin and was thought to regulates fat digestion, lipid absorption, and blood flow.,disease:A variant structure of albumin could lead to increased binding of zinc resulting in an asymptomatic augmentation of zinc concentration in the blood [MIM:194470].,disease:Defects in ALB are a cause of familial dysalbuminemic hyperthyroxinemia (FDH) [MIM:103600]. FDH is a form of euthyroid hyperthyroxinemia that is due to increased affinity of ALB for T(4). It is the most common cause of inherited euthyroid hyperthyroxinemia in Caucasian population.,function:Serum albumin, the main protein of plasma, has a good binding capacity for water, Ca(2+), Na(+), K(+), fatty acids, hormones, bilirubin and drugs. Its main function is the regulation of the collo
- Subcellular Location:
- Secreted.
- Expression:
- Plasma.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
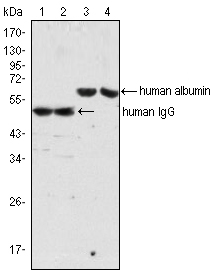
- Western Blot analysis using ALB Monoclonal Antibody (lane 3, 4) and Human IgG Monoclonal Antibody (lane 1, 2) against human serum (lane 1, 3) and plasma (lane 2, 4).



