EPO Monoclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YM0237
- Applications:WB;IF;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human
- Target:
- EPO
- Fields:
- >>Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction;>>HIF-1 signaling pathway;>>PI3K-Akt signaling pathway;>>JAK-STAT signaling pathway;>>Hematopoietic cell lineage;>>Pathways in cancer
- Gene Name:
- EPO
- Protein Name:
- Erythropoietin
- Human Gene Id:
- 2056
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P01588
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P07321
- Immunogen:
- Purified recombinant fragment of human EPO expressed in E. Coli.
- Specificity:
- EPO Monoclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of EPO protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Monoclonal, Mouse
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. IF 1:200 - 1:1000. ELISA: 1:10000. Not yet tested in other applications.
- Purification:
- Affinity purification
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- EPO;Erythropoietin;Epoetin
- Molecular Weight(Da):
- 21kD
- References:
- 1. J Negat Results Biomed. 2008 Nov 13;7:9.
2. J Biol Chem. 2009 Feb 13;284(7):4567-81.
- Background:
- This gene is a member of the EPO/TPO family and encodes a secreted, glycosylated cytokine composed of four alpha helical bundles. The protein is found in the plasma and regulates red cell production by promoting erythroid differentiation and initiating hemoglobin synthesis. This protein also has neuroprotective activity against a variety of potential brain injuries and antiapoptotic functions in several tissue types. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],
- Function:
- disease:Genetic variation in EPO is associated with susceptbility to microvascular complications of diabetes type 2 (MVCD2) [MIM:612623]; also called susceptibility to proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR) or susceptbility to diabetic end-stage renal disease (ESRD). Significant morbidity and mortality among patients with diabetes mellitus result largely from a greatly increased incidence of microvascular complications. PDR and ESRD are two of the most common and severe microvascular complications of diabetes. A high concordance exists in the development of PDR and ESRD in diabetic patients, as well as strong familial aggregation of these complications, suggesting a common underlying genetic mechanism. EPO is a potent angiogenic factor observed in the diabetic human and mouse eye.,function:Erythropoietin is the principal hormone involved in the regulation of erythrocyte differentiation
- Subcellular Location:
- Secreted .
- Expression:
- Produced by kidney or liver of adult mammals and by liver of fetal or neonatal mammals.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images

- Western Blot analysis using EPO Monoclonal Antibody against HEK293 (1) and EPO-hIgGFc transfected HEK293 (2) cell lysate.
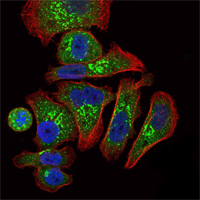
- Immunofluorescence analysis of GC7901 cells using EPO Monoclonal Antibody (green). Blue: DRAQ5 fluorescent DNA dye. Red: Actin filaments have been labeled with Alexa Fluor-555 phalloidin.



