Glycogen Synthase 1 Monoclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YM0310
- Applications:WB;FCM;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human
- Target:
- Glycogen Synthase 1
- Fields:
- >>Starch and sucrose metabolism;>>Metabolic pathways;>>PI3K-Akt signaling pathway;>>AMPK signaling pathway;>>Insulin signaling pathway;>>Glucagon signaling pathway;>>Insulin resistance;>>Diabetic cardiomyopathy
- Gene Name:
- GYS1
- Protein Name:
- Glycogen [starch] synthase muscle
- Human Gene Id:
- 2997
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P13807
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- Q9Z1E4
- Immunogen:
- Purified recombinant fragment of human Glycogen Synthase 1 expressed in E. Coli.
- Specificity:
- Glycogen Synthase 1 Monoclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of Glycogen Synthase 1 protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Monoclonal, Mouse
- Dilution:
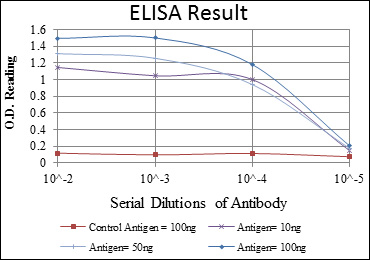
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. Flow cytometry: 1:200 - 1:400. ELISA: 1:10000. Not yet tested in other applications.
- Purification:
- Affinity purification
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- GYS1;GYS;Glycogen [starch] synthase; muscle
- Molecular Weight(Da):
- 84kD
- References:
- 1. PLoS One. 2007 Mar 14;2(3):e285.
2. Mol Syst Biol. 2007;3:89. Epub 2007 Mar 13.
- Background:
- The protein encoded by this gene catalyzes the addition of glucose monomers to the growing glycogen molecule through the formation of alpha-1,4-glycoside linkages. Mutations in this gene are associated with muscle glycogen storage disease. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene.[provided by RefSeq, Sep 2009],
- Function:
- catalytic activity:UDP-glucose ((1->4)-alpha-D-glucosyl)(n) = UDP + ((1->4)-alpha-D-glucosyl)(n+1).,disease:Defects in GYS1 are the cause of muscle glycogen storage disease type 0 (GSD0b) [MIM:611556]; also called muscle glycogen synthase deficiency. GSD0 is a metabolic disorder characterized by fasting hypoglycemia presenting in infancy or early childhood. The role of muscle glycogen is to provide critical energy during bursts of activity and sustained muscle work.,enzyme regulation:Allosteric activation by glucose-6-phosphate. Phosphorylation reduces the activity towards UDP-glucose. When in the non-phosphorylated state, glycogen synthase does not require glucose-6-phosphate as an allosteric activator; when phosphorylated it does.,function:Transfers the glycosyl residue from UDP-Glc to the non-reducing end of alpha-1,4-glucan.,pathway:Glycan biosynthesis; glycogen biosynthesis.,similar
- Subcellular Location:
- cytosol,membrane,inclusion body,
- Expression:
- Endometrium,Heart,Kidney,Lymph,Muscle,Skin,
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images

- Western Blot analysis using Glycogen Synthase 1 Monoclonal Antibody against HeLa (1) and HEK293 (2) cell lysate.
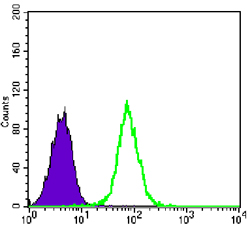
- Flow cytometric analysis of K562 cells using Glycogen Synthase 1 Monoclonal Antibody (green) and negative control (purple).