HAS1 Monoclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YM0324
- Applications:WB;IF;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human
- Target:
- HAS1
- Gene Name:
- HAS1
- Protein Name:
- Hyaluronan synthase 1
- Human Gene Id:
- 3036
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- Q8IYH3
- Immunogen:
- Purified recombinant fragment of human HAS1 expressed in E. Coli.
- Specificity:
- HAS1 Monoclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of HAS1 protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Monoclonal, Mouse
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. IF 1:200 - 1:1000. ELISA: 1:10000. Not yet tested in other applications.
- Purification:
- Affinity purification
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Molecular Weight(Da):
- 65kD
- References:
- 1. Clin Lymphoma. 2005 Mar;5(4):253-6.
2. Mol Cell Biochem. 2006 Nov;292(1-2):169-78.
3. J Biol Chem. 2008 Jun 13;283(24):16781-9.
- Background:
- Hyaluronan or hyaluronic acid (HA) is a high molecular weight unbranched polysaccharide synthesized by a wide variety of organisms from bacteria to mammals, and is a constituent of the extracellular matrix. It consists of alternating glucuronic acid and N-acetylglucosamine residues that are linked by beta-1-3 and beta-1-4 glycosidic bonds. HA is synthesized by membrane-bound synthase at the inner surface of the plasma membrane, and the chains are extruded through pore-like structures into the extracellular space. It serves a variety of functions, including space filling, lubrication of joints, and provision of a matrix through which cells can migrate. HA is actively produced during wound healing and tissue repair to provide a framework for ingrowth of blood vessels and fibroblasts. Changes in the serum concentration of HA are associated with inflammatory and degenerative arthropathies such as rheuma
- Function:
- catalytic activity:UDP-alpha-D-glucuronate + N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminyl-(1->4)-beta-D-glucuronosyl-(1->3)-(nascent hyaluronan) = UDP + beta-D-glucuronosyl-(1->3)-N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminyl-(1->4)-beta-D-glucuronosyl-(1->3)-(nascent hyaluronan).,catalytic activity:UDP-alpha-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine + beta-D-glucuronosyl-(1->3)-N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminyl-(1->4)-(nascent hyaluronan) = UDP + N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminyl-(1->4)-beta-D-glucuronosyl-(1->3)-N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminyl-(1->4)-(nascent hyaluronan).,cofactor:Magnesium.,function:Plays a role in hyaluronan/hyaluronic acid (HA) synthesis. Also able to catalyze the synthesis of chito-oligosaccharide depending on the substrate.,online information:GlycoGene database,pathway:Glycan biosynthesis; hyaluronan biosynthesis.,similarity:Belongs to the nodC/HAS family.,tissue specificity:Highly expressed in ovary followed by spleen, thymus,
- Subcellular Location:
- cytoplasm,plasma membrane,integral component of plasma membrane,integral component of membrane,
- Expression:
- Fetal brain,Lymph node,Ovary,
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
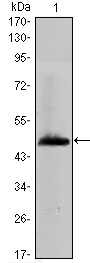
- Western Blot analysis using HAS1 Monoclonal Antibody against recombinant protein of human HAS1 (aa70-243).
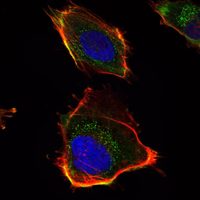
- Immunofluorescence analysis of U251 cells using HAS1 Monoclonal Antibody (green). Red: Actin filaments have been labeled with DY-554 phalloidin. Blue: DRAQ5 fluorescent DNA dye.



