Pax-6 Monoclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YM0508
- Applications:WB;FCM;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human
- Target:
- Pax-6
- Fields:
- >>Signaling pathways regulating pluripotency of stem cells;>>Maturity onset diabetes of the young
- Gene Name:
- PAX6
- Protein Name:
- Paired box protein Pax-6
- Human Gene Id:
- 5080
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P26367
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P63015
- Immunogen:
- Purified recombinant fragment of human Pax-6 expressed in E. Coli.
- Specificity:
- Pax-6 Monoclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of Pax-6 protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Monoclonal, Mouse
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. Flow cytometry: 1:200 - 1:400. ELISA: 1:10000. Not yet tested in other applications.
- Purification:
- Affinity purification
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- PAX6;AN2;Paired box protein Pax-6;Aniridia type II protein;Oculorhombin
- Molecular Weight(Da):
- 47kD
- References:
- 1.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2009 Jun;50(6):2581-90.
2.J Biol Chem. 2009 Oct 2;284(40):27524-32.
3.J Biol Chem. 2010 Jan 22;285(4):2527-36.
- Background:
- This gene encodes a homeobox and paired domain-containing protein that binds DNA and functions as a regulator of transcription. Activity of this protein is key in the development of neural tissues, particularly the eye. This gene is regulated by multiple enhancers located up to hundreds of kilobases distant from this locus. Mutations in this gene or in the enhancer regions can cause ocular disorders such as aniridia and Peter's anomaly. Use of alternate promoters and alternative splicing result in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2015],
- Function:
- developmental stage:Expressed in the developing eye and brain.,disease:Defects in PAX6 are a cause of autosomal dominant keratitis [MIM:148190]. It is an eye disorder characterized by corneal opacification and vascularization, and by foveal hypoplasia.,disease:Defects in PAX6 are a cause of bilateral optic nerve hypoplasia [MIM:165550]; also known as bilateral optic nerve aplasia. Inheritance is autosomal dominant.,disease:Defects in PAX6 are a cause of coloboma of optic nerve [MIM:120430].,disease:Defects in PAX6 are a cause of ectopia pupillae [MIM:129750]. It is a congenital eye malformation in which the pupils are displaced from their normal central position.,disease:Defects in PAX6 are a cause of foveal hypoplasia [MIM:136520]. Foveal hypoplasia can be isolated or associated with presenile cataract. Inheritance is autosomal dominant.,disease:Defects in PAX6 are a cause of Gillespie
- Subcellular Location:
- Nucleus .; [Isoform 1]: Nucleus .; [Isoform 5a]: Nucleus .
- Expression:
- [Isoform 1]: Expressed in lymphoblasts. ; [Isoform 5a]: Weakly expressed in lymphoblasts.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
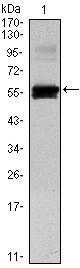
- Western Blot analysis using Pax-6 Monoclonal Antibody against recombinant Pax-6 protein (1).
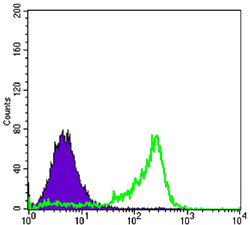
- Flow cytometric analysis of 3T3-L1 cells using Pax-6 Monoclonal Antibody (green) and negative control (purple).



