Ferritin Light Chain mouse mAb
- Catalog No.:YM1422
- Applications:ELISA
- Reactivity:Human
- Target:
- Ferritin Light Chain
- Fields:
- >>Ferroptosis;>>Necroptosis;>>Mineral absorption
- Gene Name:
- ftl
- Human Gene Id:
- 2512
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P02792
- Immunogen:
- Purified recombinant full length of human ferritin light chain protein expressed in E.coli.
- Specificity:
- This antibody detects recombinant ferritin proteins.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Monoclonal, Mouse
- Dilution:
- ELISA 1:10000-20000
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from mouse ascites by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- Ferritin L chain;Ferritin L subunit;Ferritin light chain;Ferritin light polypeptide;Ferritin light polypeptide like 3;FRIL;FRIL_HUMAN;FTL;L apoferritin;LFTD;MGC71996;NBIA 3;NBIA3.
- Observed Band(KD):
- 26kD
- Background:
- This gene encodes the light subunit of the ferritin protein. Ferritin is the major intracellular iron storage protein in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. It is composed of 24 subunits of the heavy and light ferritin chains. Variation in ferritin subunit composition may affect the rates of iron uptake and release in different tissues. A major function of ferritin is the storage of iron in a soluble and nontoxic state. Defects in this light chain ferritin gene are associated with several neurodegenerative diseases and hyperferritinemia-cataract syndrome. This gene has multiple pseudogenes. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],
- Function:
- disease:Defects in FTL are the cause of hereditary hyperferritinemia-cataract syndrome (HHCS) [MIM:600886]. It is an autosomal dominant disease characterized by early-onset bilateral cataract. Affected patients have elevated level of circulating ferritin. HHCS is caused by mutations in the iron responsive element (IRE) of the FTL gene.,disease:Defects in FTL are the cause of neuroferritinopathy [MIM:606159]; also known as adult-onset basal ganglia disease. It is a movement disorder with heterogeneous presentations starting in the fourth to sixth decade. It is characterized by a variety of neurological signs including parkinsonism, ataxia, corticospinal signs, mild nonprogressive cognitive deficit and episodic psychosis. It is linked with decreased serum ferritin levels.,function:Stores iron in a soluble, non-toxic, readily available form. Important for iron homeostasis.,function:Stores i
- Subcellular Location:
- cell,cytoplasm,cytosol,intracellular ferritin complex,membrane,autolysosome,extracellular exosome,
- Expression:
- Brain,Colon endothelium,Kidney,Liver,Placenta,Skin,Testis,Urinary bladder,
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
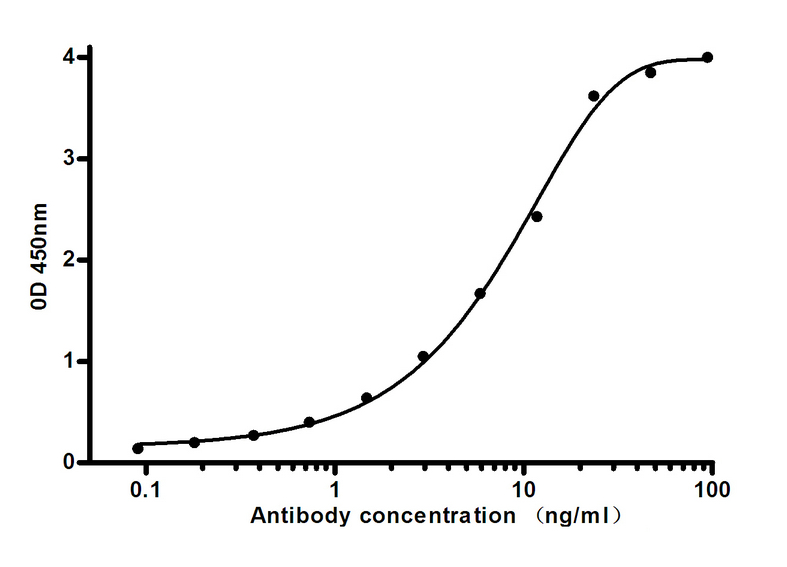
- Indirect ELISA assay for anti-Ferritin Light Chain mouse mAb.Antigen coating concentration: 4ug/ml.



