PD-1 (ABT-PD1) mouse mAb
- Catalog No.:YM4840
- Applications:IHC;WB;IF;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;
- Target:
- PD1
- Fields:
- >>Cell adhesion molecules;>>T cell receptor signaling pathway;>>PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer
- Gene Name:
- PDCD1 PD1
- Protein Name:
- Programmed cell death protein 1 (Protein PD-1) (hPD-1) (CD antigen CD279)
- Human Gene Id:
- 5133
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- Q15116
- Immunogen:
- Synthesized peptide derived from human PD-1 AA range: 1-100
- Specificity:
- The antibody can specifically recognize human PD-1 protein.
- Formulation:
- PBS, 50% glycerol, 0.05% Proclin 300, 0.05%BSA
- Source:
- Mouse, Monoclonal/IgG1, kappa
- Dilution:
- IHC 1:200-1000. WB 1:500-2000. IF 1:100-500. ELISA 1:1000-5000
- Purification:
- Protein G
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- CD279;CD279 antigen;hPD 1;hPD l;hPD-1;hSLE1;PD 1;PD-1;PD1;PDCD 1;PDCD1;PDCD1_HUMAN;Programmed cell death 1;Programmed cell death 1 protein;Programmed cell death protein 1;Protein PD 1;Protein PD-1;SLEB2;Systemic lupus erythematosus susceptibility 2
- Molecular Weight(Da):
- 32kD
- Observed Band(KD):
- 56kD
- Background:
- Programmed death-1 (PD-1) is an important immunosuppressive molecule. It is a member of CD28 superfamily. It is mainly expressed in germinal center related helper T cells and CD8 positive T cells. It includes tyrosine based inhibitory motif immune receptors, and plays an important role in peripheral immune tolerance mechanism and autoimmune diseases. PD-1 is a receptor for PD-L1 and PD-L2. Immune regulation targeting PD-1 is of great significance in anti-tumor, anti infection, anti autoimmune diseases and organ transplantation survival.
- Function:
- developmental stage:Induced at programmed cell death.,disease:Genetic variation in PDCD1 is associated with susceptibility to systemic lupus erythematosus type 2 (SLEB2) [MIM:605218]. Systemic lupus erythematosus is a chronic, inflammatory and often febrile multisystemic disorder of connective tissue. It affects principally the skin, joints, kidneys and serosal membranes. It is thought to represent a failure of the regulatory mechanisms of the autoimmune system.,function:Possible cell death inducer, in association with other factors.,similarity:Contains 1 Ig-like V-type (immunoglobulin-like) domain.,subunit:Monomer.,
- Subcellular Location:
- Membranous, Cytoplasmic
- Expression:
- Placenta,Pooled tissue,Uterine cervix,
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
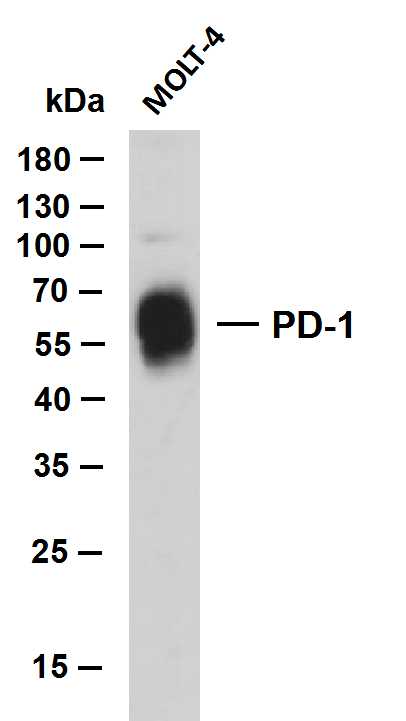
- Whole cell lysates were separated by 10% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with anti-PD-1 (ABT-PD1)antibody. The HRP-conjugated Goat anti-Mouse IgG(H + L) antibody was used to detect the antibody. Lane 1: MOLT-4
.jpg)
- Human lymphoma tissue was stained with Anti-PD-1 (ABT-PD1) Antibody
.jpg)
- Human lymphoma tissue was stained with Anti-PD-1 (ABT-PD1) Antibody
.jpg)
- Human lymphoma tissue was stained with Anti-PD-1 (ABT-PD1) Antibody

- Human tonsil tissue was stained with Anti-PD-1 (ABT-PD1) Antibody


