Cytokeratin 4 (ABT061) mouse mAb
- Catalog No.:YM4873
- Applications:IHC;WB;IF;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;
- Target:
- Cytokeratin 4
- Gene Name:
- KRT4 CYK4
- Protein Name:
- Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 4 (Cytokeratin-4) (CK-4) (Keratin-4) (K4) (Type-II keratin Kb4)
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P19013
- Immunogen:
- Synthesized peptide derived from human Cytokeratin 4 AA range: 400-534
- Specificity:
- The antibody can specifically recognize human CK4 protein, and shows no cross reaction with CK5, 6, 7, 8, 14, 15, 17, 20.
- Formulation:
- PBS, 50% glycerol, 0.05% Proclin 300, 0.05%BSA
- Source:
- Mouse, Monoclonal/IgG1, kappa
- Dilution:
- IHC 1:200-1000. WB 1:500-2000. IF 1:100-500. ELISA 1:1000-5000
- Purification:
- Protein G
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- CK 4;CK-4;CK4;CYK4;Cytokeratin 4;CytokeRatin-4;CytokeRatin4;FLJ31692;K2C4_HUMAN;K4;KeRatin 4;KeRatin;KeRatin type II cytoskeletal 4;KeRatin-4;KeRatin4;KRT 4;Krt4;type II cytoskeletal 4;Type-II keRatin Kb4
- Molecular Weight(Da):
- 57kD
- Observed Band(KD):
- 57kD
- Background:
- CK4 is a cytokeratin with a molecular weight of 59 kDa. It is a member of type II cytokeratin family. CK4 is widely expressed in non keratinocytes and stratified squamous epithelium. It is mainly used to label esophageal and oral squamous epithelial cells and tumors of their origin.
- Function:
- disease:Defects in KRT4 are a cause of white sponge nevus of cannon (WSN) [MIM:193900]. WSN is a rare autosomal dominant disorder which predominantly affects non-cornified stratified squamous epithelia. Clinically, it is characterized by the presence of soft, white, and spongy plaques in the oral mucosa. The characteristic histopathologic features are epithelial thickening, parakeratosis, and vacuolization of the suprabasal layer of oral epithelial keratinocytes. Less frequently the mucous membranes of the nose, esophagus, genitalia and rectum are involved.,miscellaneous:There are two types of cytoskeletal and microfibrillar keratin: I (acidic; 40-55 kDa) and II (neutral to basic; 56-70 kDa).,polymorphism:Three alleles of K4 are known: K4A2 (shown here), K4A1 and K4B.,similarity:Belongs to the intermediate filament family.,subunit:Heterotetramer of two type I and two type II keratins. Ke
- Subcellular Location:
- Cytoplasmic, Membranous
- Expression:
- Detected in the suprabasal layer of the stratified epithelium of the esophagus, exocervix, vagina, mouth and lingual mucosa, and in cells and cell clusters in the mucosa and serous gland ducts of the esophageal submucosa (at protein level). Expressed widely in the exocervix and esophageal epithelium, with lowest levels detected in the basal cell layer.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
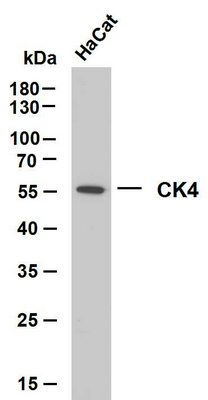
- HaCat whole cell lysates were separated by 10% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with anti-CK4(ABT061) antibody. The HRP-conjugated Goat anti-Mouse IgG(H + L) antibody was used to detect the antibody. Lane 1: HaCat
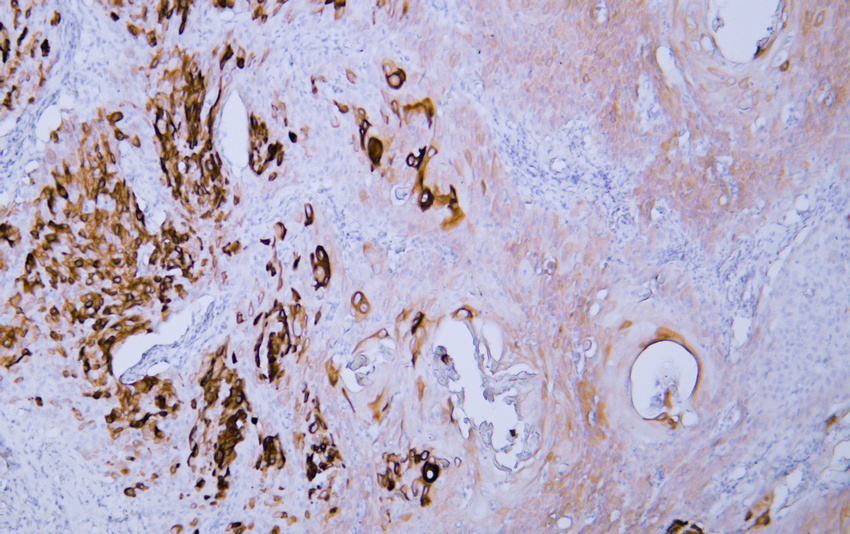
- Human cervical squamous cell carcinoma tissue was stained with Anti-Cytokeratin 4 (ABT061) Antibody
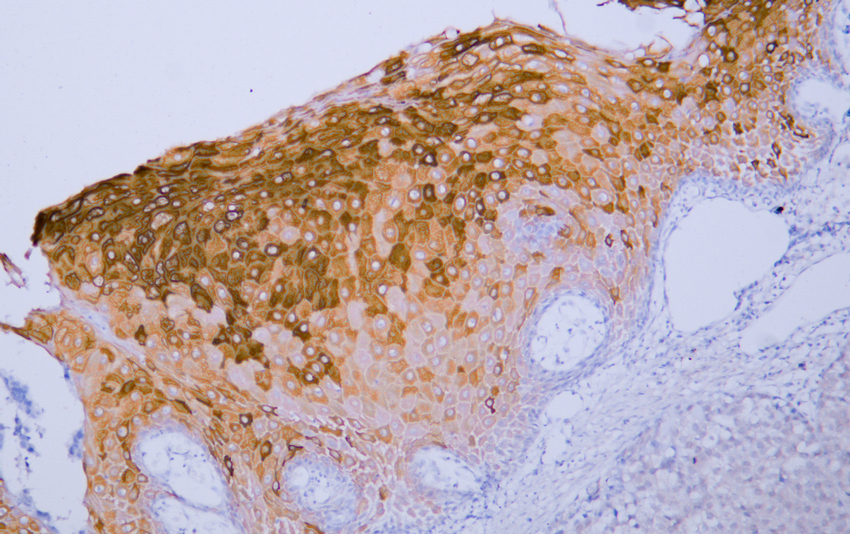
- Human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma tissue was stained with Anti-Cytokeratin 4 (ABT061) Antibody
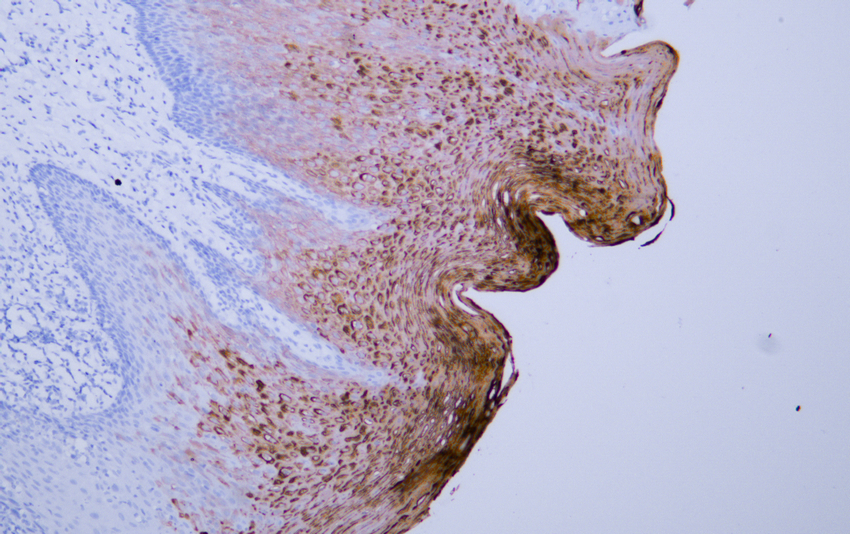
- Human oral squamous cell carcinoma tissue was stained with Anti-Cytokeratin 4 (ABT061) Antibody



