CD68 (ABT-CD68) mouse mAb
- Catalog No.:YM6022
- Applications:IHC;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;
- Target:
- CD68
- Fields:
- >>Lysosome
- Gene Name:
- CD68
- Protein Name:
- Macrosialin (Gp110) (CD antigen CD68)
- Human Gene Id:
- 968
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P34810
- Immunogen:
- Synthesized peptide derived from human CD68 AA range: 250-354
- Specificity:
- The antibody can specifically recognize human CD68 protein.
- Formulation:
- PBS, 50% glycerol, 0.05% Proclin 300, 0.05%BSA
- Source:
- Mouse, Monoclonal/IgG1, kappa
- Dilution:
- IHC 1:50-200. ELISA 1:500-5000
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from ascites by affinity-chromatography using specific immunogen.
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Molecular Weight(Da):
- 35kD
- Observed Band(KD):
- 100-110kD
- Background:
- This gene encodes a 110-kD transmembrane glycoprotein that is highly expressed by human monocytes and tissue macrophages. It is a member of the lysosomal/endosomal-associated membrane glycoprotein (LAMP) family. The protein primarily localizes to lysosomes and endosomes with a smaller fraction circulating to the cell surface. It is a type I integral membrane protein with a heavily glycosylated extracellular domain and binds to tissue- and organ-specific lectins or selectins. The protein is also a member of the scavenger receptor family. Scavenger receptors typically function to clear cellular debris, promote phagocytosis, and mediate the recruitment and activation of macrophages. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcripts encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],
- Function:
- function:Could play a role in phagocytic activities of tissue macrophages, both in intracellular lysosomal metabolism and extracellular cell-cell and cell-pathogen interactions. Bind to tissue- and organ-specific lectins or selectins, allowing homing of macrophage subsets to particular sites. Rapid recirculation of CD68 from endosomes, lysosomes to the plasma membrane may allow macrophages to crawl over selectin bearing substrates or other cells.,PTM:N- and O-glycosylated.,similarity:Belongs to the LAMP family.,tissue specificity:Highly expressed by blood monocytes and tissue macrophages. Also expressed in many tumor cell lines which could allow them to attach to selectins on vascular endothelium, facilitating their dissemination to secondary sites.,
- Subcellular Location:
- Cytoplasmic, Membranous
- Expression:
- Highly expressed by blood monocytes and tissue macrophages. Also expressed in lymphocytes, fibroblasts and endothelial cells. Expressed in many tumor cell lines which could allow them to attach to selectins on vascular endothelium, facilitating their dissemination to secondary sites.
Single-Cell RNA Sequencing to Dissect the Immunological Network of Autoimmune Myocarditis. CIRCULATION 2020 May 20 IHC Human cardiac cell
Xiao, Jun-bo, et al. "Novel Insight: CUEDC2 Expression of Potential Prognostic Value in Esophageal Squamous Cell Cancer." (2020).
Genetic and pharmacological targeting of GSDMD ameliorates systemic inflammation in macrophage activation syndrome
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
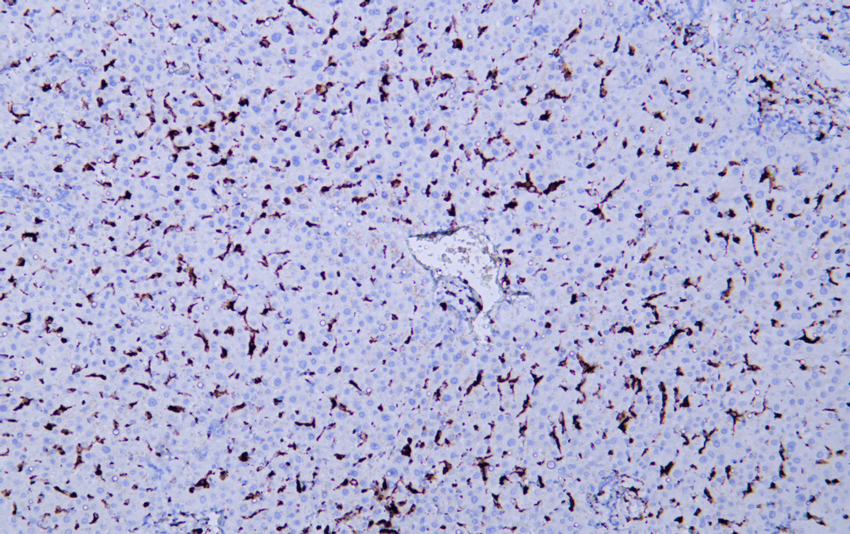
- Human liver tissue was stained with Anti-CD68 (ABT-CD68) Antibody
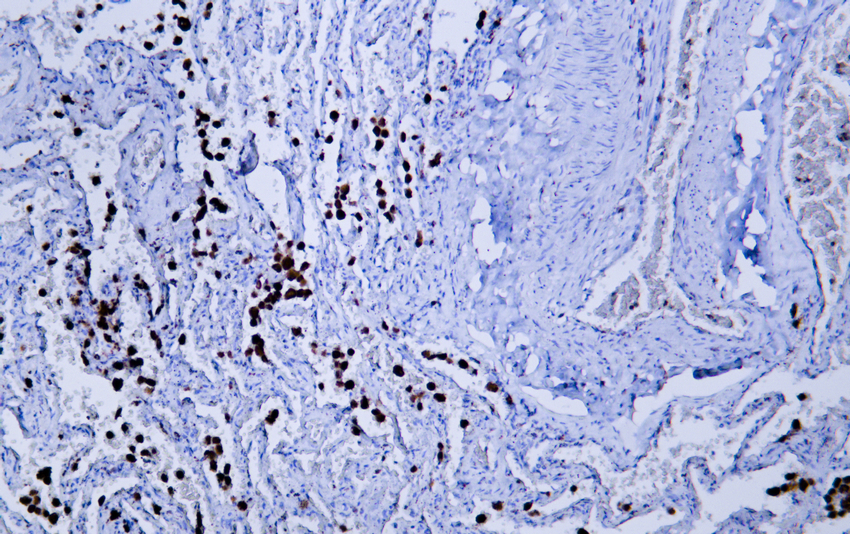
- Human lung tissue was stained with Anti-CD68 (ABT-CD68) Antibody
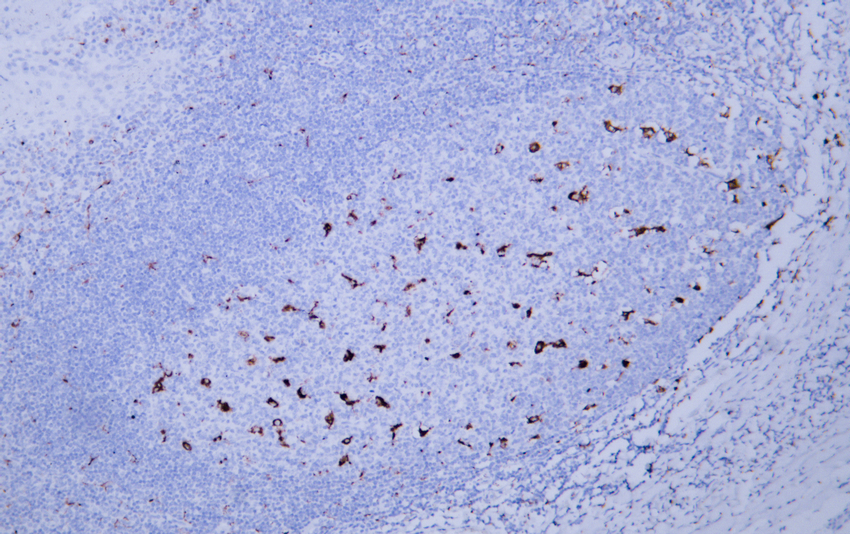
- Human tonsil tissue was stained with Anti-CD68 (ABT-CD68) Antibody
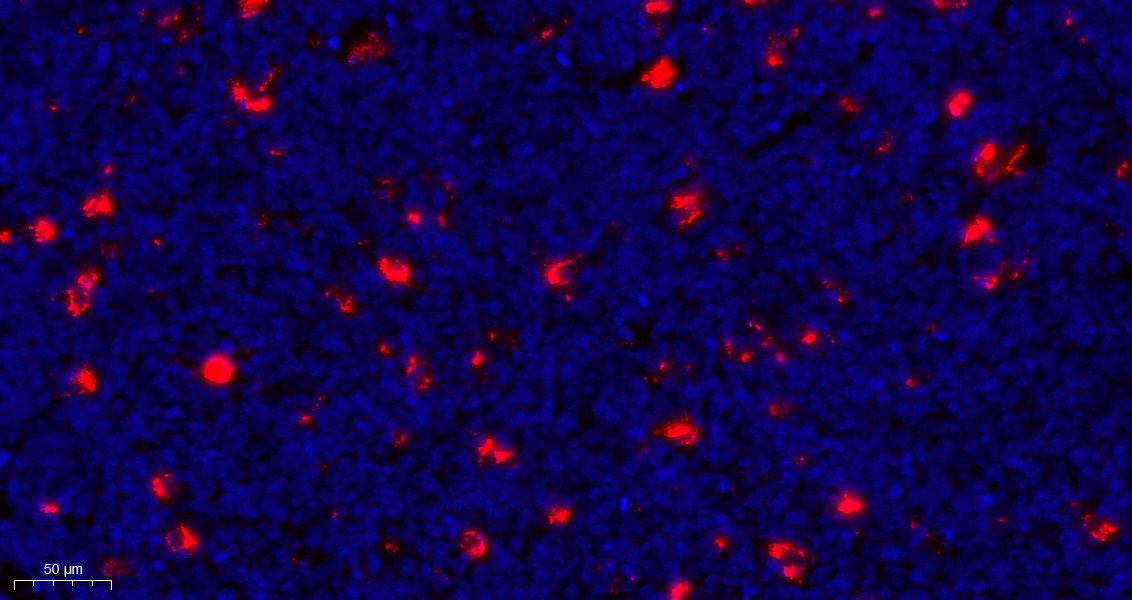
- Immunofluorescence analysis of paraffin-embedded human tonsil. Primary Antibody was diluted at 1:200(4° overnight). an Multi colour-Fluorescence kit (RS0035, Immunoway). EDTA based antigen retrieval was used before Red tyramide signal amplification. DAPI (dark blue) was used as a nuclear counter stain. Microscopy and pseudocoloring of individual dyes was performed using a Slideviewer Imaging System (3D histech).



