Actin, Muscle Specific (ABT-MSA) Mouse mAb
- Catalog No.:YM6142
- Applications:IHC;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat;Monkey;Bovin;Pig;Chick;
- Target:
- Actin, Muscle Specific
- Fields:
- >>Cardiac muscle contraction;>>Adrenergic signaling in cardiomyocytes;>>Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy;>>Dilated cardiomyopathy
- Gene Name:
- Actin, Muscle Specific
- Protein Name:
- Actin, Muscle Specific
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P68032/P68133/P63267/P62736
- Immunogen:
- Synthesized peptide derived from human Actin, Muscle Specific AA range: 2-50
- Specificity:
- The antibody can specifically recognize proteins from smooth muscle, myocardium and skeletal muscle α actin and smooth muscle derived γ actin, and β actin or non smooth muscle derived γ actin does not
- Formulation:
- PBS, 50% glycerol, 0.05% Proclin 300, 0.05%BSA
- Source:
- Mouse, Monoclonal/IgG1, kappa
- Dilution:
- IHC 1:200-400. ELISA 1:500-5000
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from ascites by affinity-chromatography using specific immunogen.
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Observed Band(KD):
- 42kD
- Background:
- Actins are highly conserved proteins that are involved in various types of cell motility. Polymerization of globular actin (G-actin) leads to a structural filament (F-actin) in the form of a two-stranded helix. Each actin can bind to four others. The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the actin family which is comprised of three main groups of actin isoforms, alpha, beta, and gamma. The alpha actins are found in muscle tissues and are a major constituent of the contractile apparatus. Defects in this gene have been associated with idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy (IDC) and familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (FHC). [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],
- Function:
- disease:Defects in ACTC1 are the cause of cardiomyopathy dilated type 1R (CMD1R) [MIM:102540]. Dilated cardiomyopathy is a disorder characterized by ventricular dilation and impaired systolic function, resulting in congestive heart failure and arrhythmia. Patients are at risk of premature death.,disease:Defects in ACTC1 are the cause of cardiomyopathy familial hypertrophic type 11 (CMH11) [MIM:612098]. Familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is a hereditary heart disorder characterized by ventricular hypertrophy, which is usually asymmetric and often involves the interventricular septum. The symptoms include dyspnea, syncope, collapse, palpitations, and chest pain. They can be readily provoked by exercise. The disorder has inter- and intrafamilial variability ranging from benign to malignant forms with high risk of cardiac failure and sudden cardiac death.,function:Actins are highly conserv
- Subcellular Location:
- Cytoplasmic
- Expression:
- Muscle,Tongue,
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images

- Human appendix tissue was stained with anti-MSA(ABT-MSA) antibody.

- Human cardiac muscle tissue was stained with anti-MSA(ABT-MSA) antibody.

- Human leiomyoma tissue was stained with anti-MSA(ABT-MSA) antibody.

- Human rhabdomyosarcoma tissue was stained with anti-MSA(ABT-MSA) antibody.
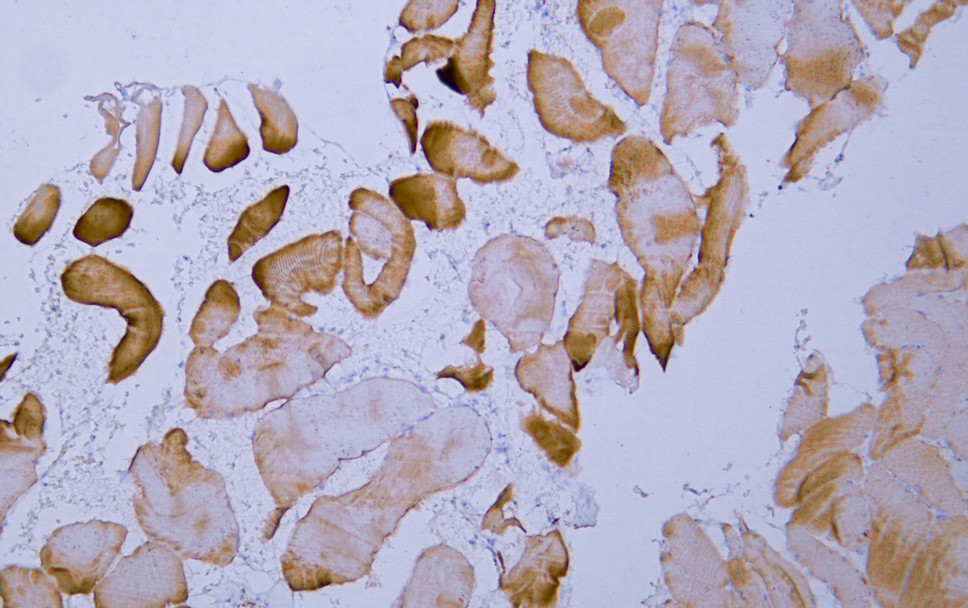
- Human skeletal muscle tissue was stained with anti-MSA(ABT-MSA) antibody.



