Cytokeratin 1 (ABT-CK1) mouse mAb
- Catalog No.:YM6160
- Applications:IHC;IF;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;
- Target:
- Cytokeratin 1
- Gene Name:
- KRT1 KRTA
- Protein Name:
- Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 1 (67 kDa cytokeratin) (Cytokeratin-1) (CK-1) (Hair alpha protein) (Keratin-1) (K1) (Type-II keratin Kb1)
- Human Gene Id:
- 3848
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P04264
- Immunogen:
- Synthesized peptide derived from human Cytokeratin 1 AA range: 200-300
- Specificity:
- The antibody can specifically recognize human CK1 protein. In immunohistochemistry on formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue sections, the antibody specifically labels only skin epidermal cells, whe
- Formulation:
- PBS, 50% glycerol, 0.05% Proclin 300, 0.05%BSA
- Source:
- Mouse, Monoclonal/IgG1, kappa
- Dilution:
- IHC 1:200-400. IF 1:50-200. ELISA 1:500-5000
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from ascites by affinity-chromatography using specific immunogen.
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Molecular Weight(Da):
- 66kD
- Background:
- keratin 1(KRT1) Homo sapiens The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the keratin gene family. The type II cytokeratins consist of basic or neutral proteins which are arranged in pairs of heterotypic keratin chains coexpressed during differentiation of simple and stratified epithelial tissues. This type II cytokeratin is specifically expressed in the spinous and granular layers of the epidermis with family member KRT10 and mutations in these genes have been associated with bullous congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma. The type II cytokeratins are clustered in a region of chromosome 12q12-q13. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],
- Function:
- disease:Defects in KRT1 are a cause of bullous congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma (BCIE) [MIM:113800]; also known as epidermolytic hyperkeratosis (EHK) or bullous erythroderma ichthyosiformis congenita of Brocq. BCIE is an autosomal dominant skin disorder characterized by widespread blistering and an ichthyotic erythroderma at birth that persist into adulthood. Histologically there is a diffuse epidermolytic degeneration in the lower spinous layer of the epidermis. Within a few weeks from birth, erythroderma and blister formation diminish and hyperkeratoses develop.,disease:Defects in KRT1 are a cause of ichthyosis annular epidermolytic (AEI) [MIM:607602]; also known as cyclic ichthyosis with epidermolytic hyperkeratosis. AEI is a skin disorder resembling bullous congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma. Affected individuals present with bullous ichthyosis in early childhood and hyperker
- Subcellular Location:
- Cytoplasmic, Membranous
- Expression:
- The source of this protein is neonatal foreskin. The 67-kDa type II keratins are expressed in terminally differentiating epidermis.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
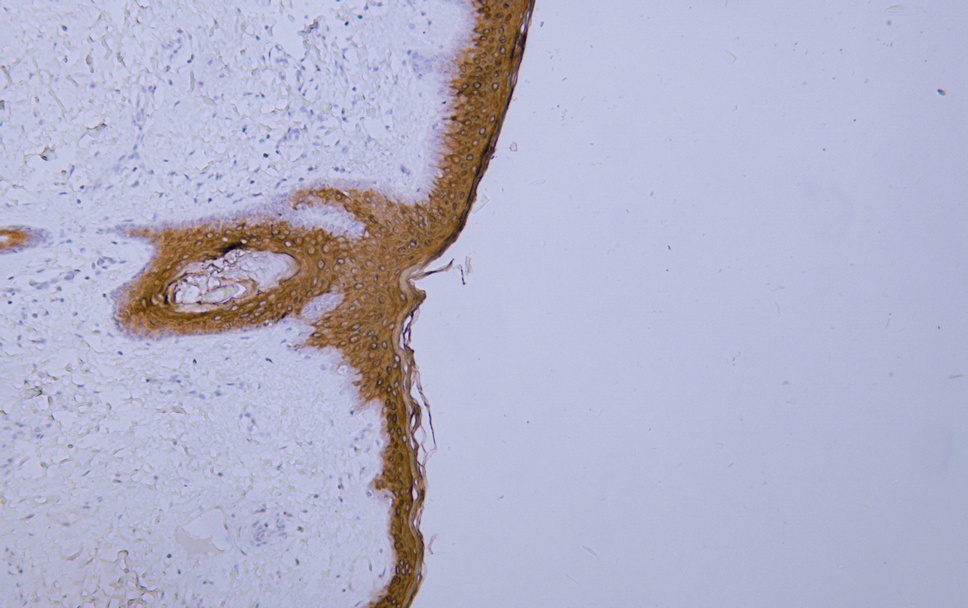
- Human skin tissue was stained with Anti-Cytokeratin 1 (ABT-CK1) Antibody
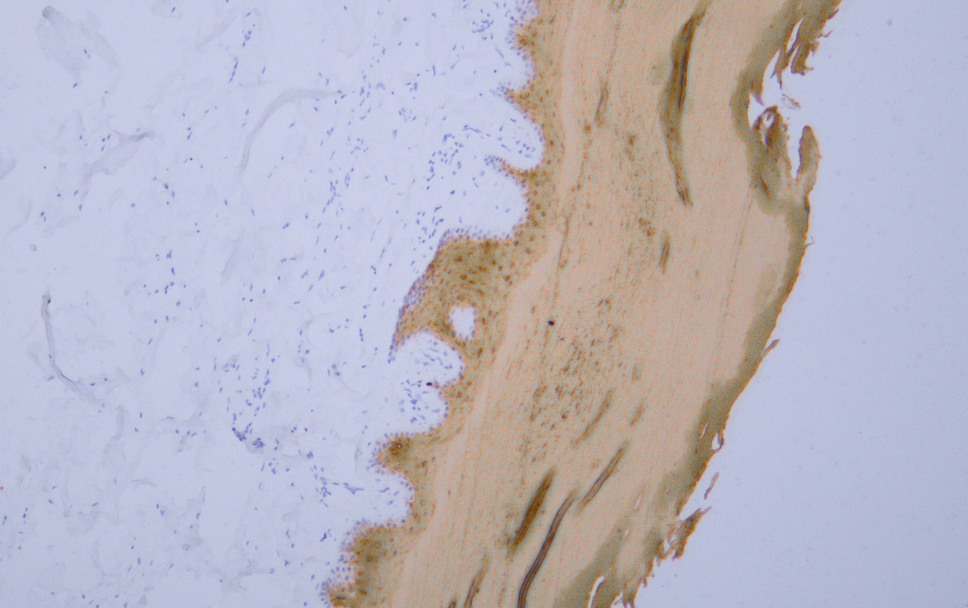
- Human skin tissue was stained with Anti-Cytokeratin 1 (ABT-CK1) Antibody



