MutS Protein Homolog 6(MSH6) (ABT-MSH6) mouse mAb
- Catalog No.:YM6195
- Applications:IHC;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;
- Target:
- MSH6
- Fields:
- >>Platinum drug resistance;>>Mismatch repair;>>Pathways in cancer;>>Colorectal cancer
- Gene Name:
- MSH6 GTBP
- Protein Name:
- DNA mismatch repair protein Msh6 (hMSH6) (G/T mismatch-binding protein) (GTBP) (GTMBP) (MutS-alpha 160 kDa subunit) (p160)
- Human Gene Id:
- 2956
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P52701
- Immunogen:
- Synthesized peptide derived from human MutS Protein Homolog 6(MSH6) AA range: 900-1000
- Specificity:
- The antibody can specifically recognize human MSH6 protein.
- Formulation:
- PBS, 50% glycerol, 0.05% Proclin 300, 0.05%BSA
- Source:
- Mouse, Monoclonal/IgG1, kappa
- Dilution:
- IHC 1:50-100. ELISA 1:500-5000
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from ascites by affinity-chromatography using specific immunogen.
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Molecular Weight(Da):
- 153kD
- Observed Band(KD):
- 180kD
- Background:
- This gene encodes a member of the DNA mismatch repair MutS family. In E. coli, the MutS protein helps in the recognition of mismatched nucleotides prior to their repair. A highly conserved region of approximately 150 aa, called the Walker-A adenine nucleotide binding motif, exists in MutS homologs. The encoded protein heterodimerizes with MSH2 to form a mismatch recognition complex that functions as a bidirectional molecular switch that exchanges ADP and ATP as DNA mismatches are bound and dissociated. Mutations in this gene may be associated with hereditary nonpolyposis colon cancer, colorectal cancer, and endometrial cancer. Transcripts variants encoding different isoforms have been described. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2013],
- Function:
- disease:Defects in MSH6 are a cause of susceptibility to endometrial cancer [MIM:608089].,disease:Defects in MSH6 are the cause of hereditary non-polyposis colorectal cancer type 5 (HNPCC5) [MIM:600678]. Mutations in more than one gene locus can be involved alone or in combination in the production of the HNPCC phenotype (also called Lynch syndrome). Most families with clinically recognized HNPCC have mutations in either MLH1 or MSH2 genes. HNPCC is an autosomal, dominantly inherited disease associated with marked increase in cancer susceptibility. It is characterized by a familial predisposition to early onset colorectal carcinoma (CRC) and extra-colonic cancers of the gastrointestinal, urological and female reproductive tracts. HNPCC is reported to be the most common form of inherited colorectal cancer in the Western world. Cancers in HNPCC originate within benign neoplastic polyps ter
- Subcellular Location:
- Nuclear
- Expression:
- Epithelium,Placenta,Pooled,Testis,
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
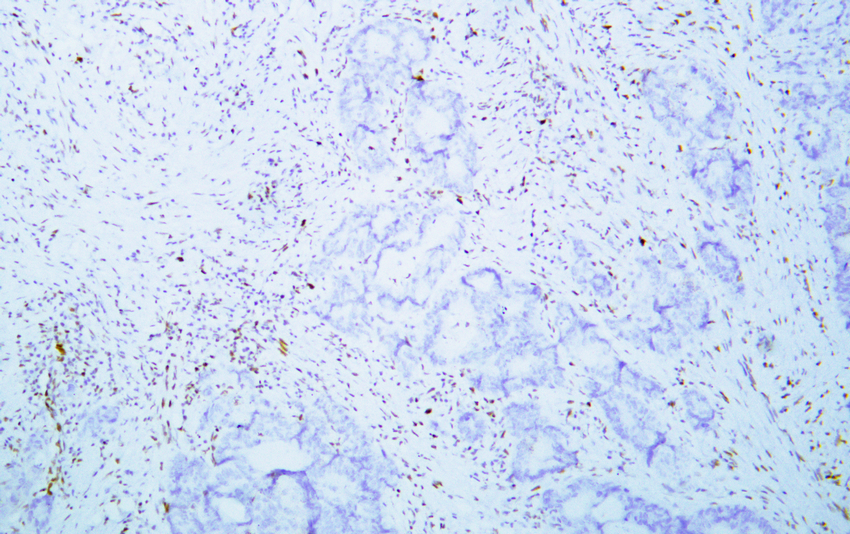
- Human colon adenocarcinoma tissue with loss of MSH6 expression was stained with Anti-MSH6 (ABT-MSH6) Antibody
.jpg)
- Human colon carcinoma tissue was stained with Anti-MSH6 (ABT-MSH6) Antibody
.jpg)
- Human colon carcinoma tissue was stained with Anti-MSH6 (ABT-MSH6) Antibody
.jpg)
- Human colon carcinoma tissue was stained with Anti-MSH6 (ABT-MSH6) Antibody
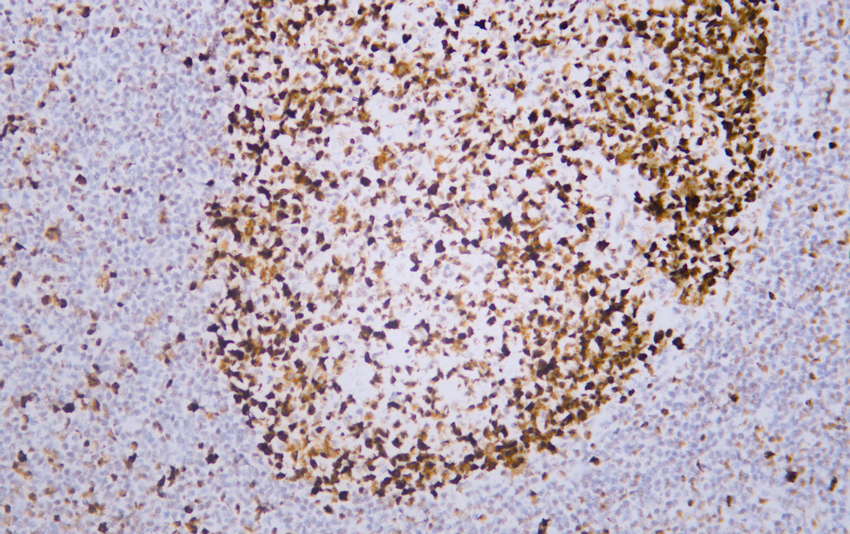
- Human tonsil tissue was stained with Anti-MSH6 (ABT-MSH6) Antibody



