NSE (ABT-NSE) mouse mAb (Ready to Use)
- Catalog No.:YM6754R
- Applications:IHC
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat;
- Target:
- Enolase
- Fields:
- >>Glycolysis / Gluconeogenesis;>>Metabolic pathways;>>Carbon metabolism;>>Biosynthesis of amino acids;>>RNA degradation;>>HIF-1 signaling pathway
- Gene Name:
- ENO2
- Protein Name:
- Neuron-Specific Enolase(NSE)
- Human Gene Id:
- 2026
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P09104
- Immunogen:
- Synthesized peptide derived from human Neuron-Specific Enolase(NSE) AA range: 300-434
- Specificity:
- The antibody can specifically recognize human NSE protein.
- Formulation:
- The prediluted ready-to-use antibody is diluted in phosphate buffer saline containing stabilizing protein and 0.05% Proclin 300
- Source:
- Mouse, Monoclonal/IgG2a, kappa
- Dilution:
- Ready to use for IHC
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from ascites by affinity-chromatography using specific immunogen.
- Storage Stability:
- 2°C to 8°C/1 year
- Other Name:
- Gamma-enolase (EC 4.2.1.11;2-phospho-D-glycerate hydro-lyase;Enolase 2;Neural enolase;Neuron-specific enolase;NSE)
- Background:
- enolase 2(ENO2) Homo sapiens This gene encodes one of the three enolase isoenzymes found in mammals. This isoenzyme, a homodimer, is found in mature neurons and cells of neuronal origin. A switch from alpha enolase to gamma enolase occurs in neural tissue during development in rats and primates. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],
- Function:
- catalytic activity:2-phospho-D-glycerate = phosphoenolpyruvate + H(2)O.,cofactor:Magnesium. Required for catalysis and for stabilizing the dimer.,developmental stage:During ontogenesis, there is a transition from the alpha/alpha homodimer to the alpha/beta heterodimer in striated muscle cells, and to the alpha/gamma heterodimer in nerve cells.,function:Has neurotrophic and neuroprotective properties on a broad spectrum of central nervous system (CNS) neurons. Binds, in a calcium-dependent manner, to cultured neocortical neurons and promotes cell survival.,induction:Levels of ENO2 increase dramatically in cardiovascular accidents, cerebral trauma, brain tumors and Creutzfeldt-Jacob disease.,pathway:Carbohydrate degradation; glycolysis; pyruvate from D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate: step 4/5.,similarity:Belongs to the enolase family.,subcellular location:Can translocate to the plasma membrane
- Subcellular Location:
- Cytoplasmic
- Expression:
- The alpha/alpha homodimer is expressed in embryo and in most adult tissues. The alpha/beta heterodimer and the beta/beta homodimer are found in striated muscle, and the alpha/gamma heterodimer and the gamma/gamma homodimer in neurons.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
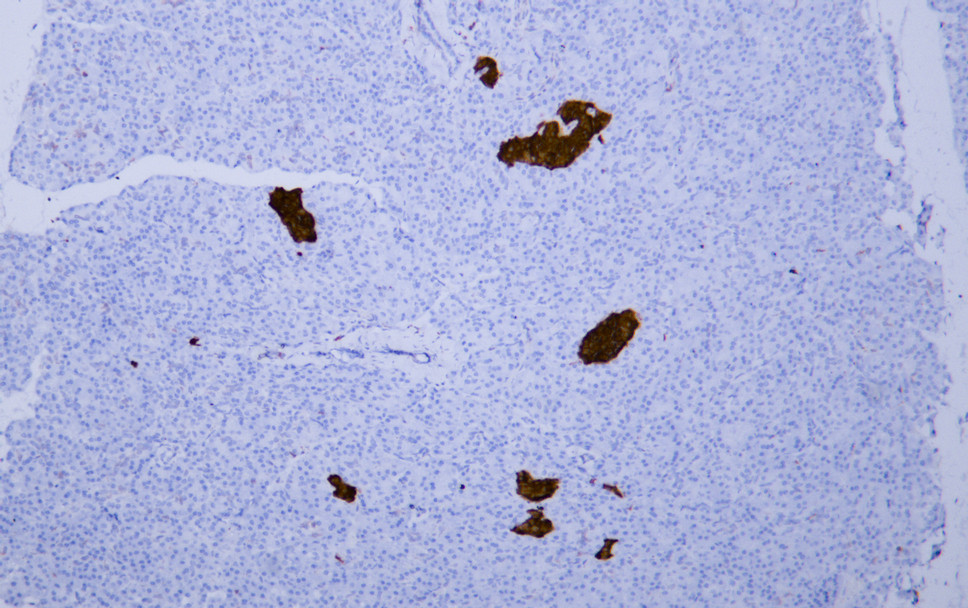
- Human pancreas tissue was stained with Anti-Neuron-Specific Enolase (ABT-NSE) Antibody



