CD8 a (ABT155) mouse mAb
- Catalog No.:YM6846
- Applications:IHC;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;
- Target:
- CD8
- Fields:
- >>Cell adhesion molecules;>>Antigen processing and presentation;>>Hematopoietic cell lineage;>>T cell receptor signaling pathway;>>Yersinia infection;>>Primary immunodeficiency
- Gene Name:
- CD8A MAL
- Protein Name:
- CD8 a
- Human Gene Id:
- 925
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P01732
- Immunogen:
- Synthesized peptide derived from human CD8 a AA range: 100-235
- Specificity:
- The antibody can specifically recognize human CD8 protein, including two typies of dimer: αβ heterodimer or αα homodimer.
- Formulation:
- PBS, 50% glycerol, 0.05% Proclin 300, 0.05%BSA
- Source:
- Mouse, Monoclonal/IgG2a, kappa
- Dilution:
- IHC 1:200-400. ELISA 1:500-5000
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from ascites by affinity-chromatography using specific immunogen.
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- T-cell surface glycoprotein CD8 alpha chain (T-lymphocyte differentiation antigen T8/Leu-2;CD antigen CD8a)
- Molecular Weight(Da):
- 26kD
- Observed Band(KD):
- 30-35kD
- Background:
- The CD8 antigen is a cell surface glycoprotein found on most cytotoxic T lymphocytes that mediates efficient cell-cell interactions within the immune system. The CD8 antigen acts as a coreceptor with the T-cell receptor on the T lymphocyte to recognize antigens displayed by an antigen presenting cell in the context of class I MHC molecules. The coreceptor functions as either a homodimer composed of two alpha chains or as a heterodimer composed of one alpha and one beta chain. Both alpha and beta chains share significant homology to immunoglobulin variable light chains. This gene encodes the CD8 alpha chain. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2011],
- Function:
- disease:Defects in CD8A are a cause of familial CD8 deficiency (CD8 deficiency) [MIM:608957]. Familial CD8 deficiency is a novel autosomal recessive immunologic defect characterized by absence of CD8+ cells, leading to recurrent bacterial infections.,function:Identifies cytotoxic/suppressor T-cells that interact with MHC class I bearing targets. CD8 is thought to play a role in the process of T-cell mediated killing. CD8 alpha chains binds to class I MHC molecules alpha-3 domains.,online information:CD8 entry,online information:CD8A mutation db,PTM:All of the five most carboxyl-terminal cysteines form inter-chain disulfide bonds in dimers and higher multimers, while the four N-terminal cysteines do not.,similarity:Contains 1 Ig-like V-type (immunoglobulin-like) domain.,subunit:In general heterodimer of an alpha and a beta chain linked by two disulfide bonds. Can also form homodimers. Sho
- Subcellular Location:
- Membranous
- Expression:
- CD8 on thymus-derived T-cells usually consists of a disulfide-linked alpha/CD8A and a beta/CD8B chain. Less frequently, CD8 can be expressed as a CD8A homodimer. A subset of natural killer cells, memory T-cells, intraepithelial lymphocytes, monocytes and dendritic cells expresses CD8A homodimers. Expressed at the cell surface of plasmacytoid dendritic cells upon herpes simplex virus-1 stimulation.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images

- Human burkitt lymphoma tissue was stained with Anti-CD8 (ABT155) Antibody

- Human lymphoma tissue was stained with Anti-CD8 (ABT155) Antibody.
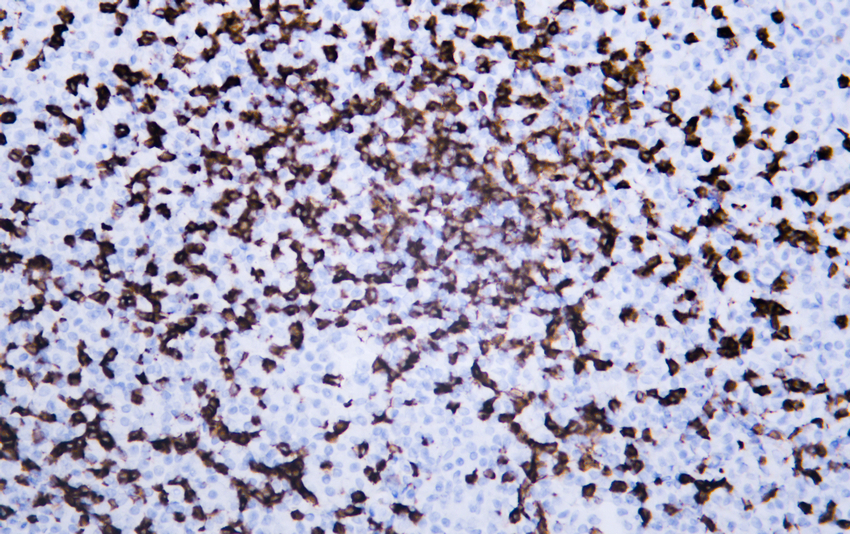
- Human lymphoma tissue was stained with Anti-CD8 (ABT155) Antibody. Polymer HRP Goat Anti Mouse/Rabbit IgG(H+L) Antibody was used at 37°C 30 minutes.

- Human tonsil tissue was stained with Anti-CD8 (ABT155) Antibody

- Human tonsil tissue was stained with Anti-CD8 (ABT155) Antibody



