HSP60 (ABT186) mouse mAb
- Catalog No.:YM6884
- Applications:IHC;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat;
- Target:
- Hsp60
- Fields:
- >>RNA degradation;>>Type I diabetes mellitus;>>Legionellosis;>>Tuberculosis;>>Lipid and atherosclerosis
- Gene Name:
- MAPK7
- Protein Name:
- HSP60
- Human Gene Id:
- 3329
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P10809
- Immunogen:
- Synthesized peptide derived from human HSP60 AA range: 500-573
- Specificity:
- The antibody can specifically recognize human HSP60 protein.
- Formulation:
- PBS, 50% glycerol, 0.05% Proclin 300, 0.05%BSA
- Source:
- Mouse, Monoclonal/IgG2b, kappa
- Dilution:
- IHC 1:200-400. ELISA 1:500-5000
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from ascites by affinity-chromatography using specific immunogen.
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- 60 kDa heat shock protein, mitochondrial (60 kDa chaperonin;Chaperonin 60;CPN60;Heat shock protein 60;HSP-60;Hsp60;HuCHA60;Mitochondrial matrix protein P1;P60 lymphocyte protein)
- Molecular Weight(Da):
- 60kD
- Observed Band(KD):
- 60kD
- Background:
- This gene encodes a member of the chaperonin family. The encoded mitochondrial protein may function as a signaling molecule in the innate immune system. This protein is essential for the folding and assembly of newly imported proteins in the mitochondria. This gene is adjacent to a related family member and the region between the 2 genes functions as a bidirectional promoter. Several pseudogenes have been associated with this gene. Two transcript variants encoding the same protein have been identified for this gene. Mutations associated with this gene cause autosomal recessive spastic paraplegia 13. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2010],
- Function:
- disease:Defects in HSPD1 are a cause of spastic paraplegia autosomal dominant type 13 (SPG13) [MIM:605280]. Spastic paraplegia is a degenerative spinal cord disorder characterized by a slow, gradual, progressive weakness and spasticity of the lower limbs.,disease:Defects in HSPD1 are the cause of leukodystrophy hypomyelinating type 4 (HLD4) [MIM:612233]; also called mitochondrial HSP60 chaperonopathy or MitCHAP-60 disease. HLD4 is a severe autosomal recessive hypomyelinating leukodystrophy. Clinically characterized by infantile-onset rotary nystagmus, progressive spastic paraplegia, neurologic regression, motor impairment, profound mental retardation. Death usually occurrs within the first 2 decades of life.,function:Implicated in mitochondrial protein import and macromolecular assembly. May facilitate the correct folding of imported proteins. May also prevent misfolding and promote the
- Subcellular Location:
- Cytoplasmic
- Expression:
- Cytoplasmic
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images

- Human breast carcinoma tissue was stained with Anti-HSP60 (ABT186) Antibody
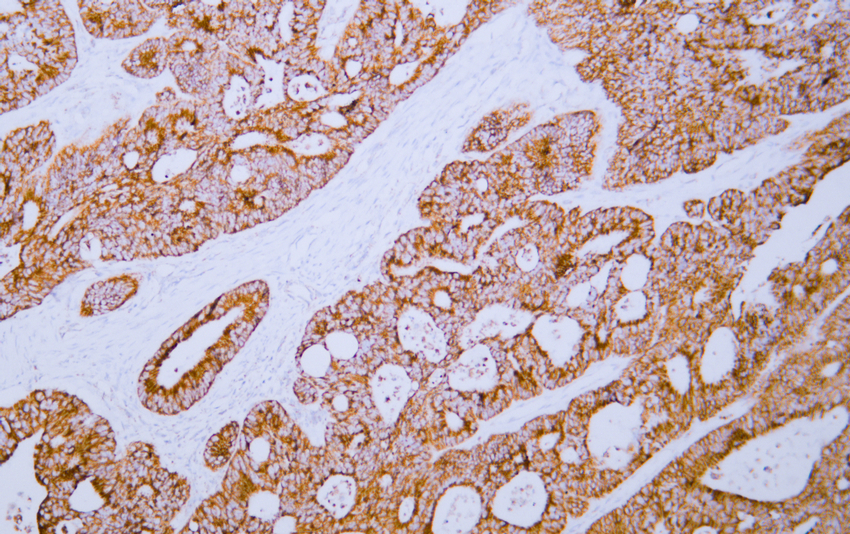
- Human colon carcinoma tissue was stained with Anti-HSP60 (ABT186) Antibody
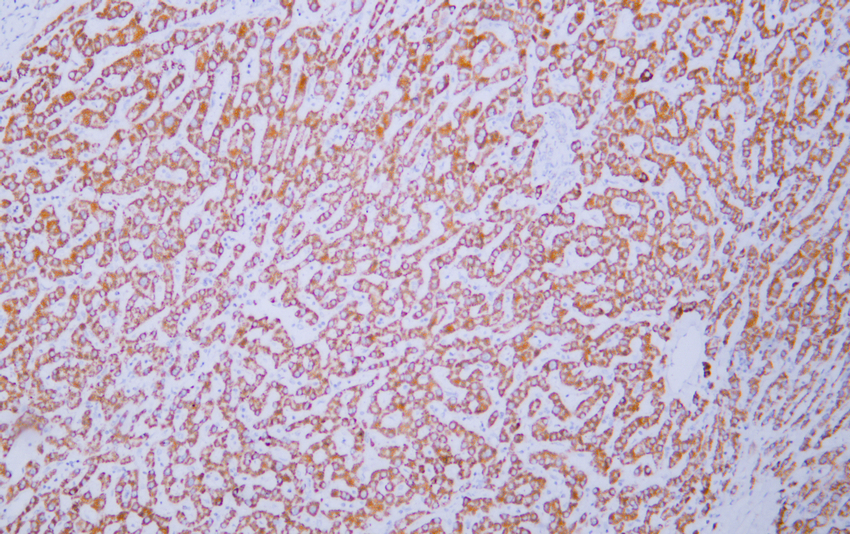
- Human hepatocellular carcinoma tissue was stained with Anti-HSP60 (ABT186) Antibody

- Human kidney tissue was stained with Anti-HSP60 (ABT186) Antibody

- Human liver tissue was stained with Anti-HSP60 (ABT186) Antibody



