Neurofilament (ABT456) mouse mAb (Ready to Use)
- Catalog No.:YM6897R
- Applications:IHC
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat;
- Target:
- NF-L
- Fields:
- >>Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis;>>Pathways of neurodegeneration - multiple diseases
- Gene Name:
- NEFL NF68 NFL
- Protein Name:
- Neurofilament
- Human Gene Id:
- 4747
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P07196
- Immunogen:
- Synthesized peptide derived from human Neurofilament AA range: 400-543
- Specificity:
- The antibody can specifically recognize human Neurofilament protein, especilaly NF-L protein.
- Formulation:
- The prediluted ready-to-use antibody is diluted in phosphate buffer saline containing stabilizing protein and 0.05% Proclin 300
- Source:
- Mouse, Monoclonal/IgG1, kappa
- Dilution:
- Ready to use for IHC
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from ascites by affinity-chromatography using specific immunogen.
- Storage Stability:
- 2°C to 8°C/1 year
- Other Name:
- Neurofilament light polypeptide (NF-L;68 kDa neurofilament protein;Neurofilament triplet L protein)
- Background:
- Neurofilaments are type IV intermediate filament heteropolymers composed of light, medium, and heavy chains. Neurofilaments comprise the axoskeleton and they functionally maintain the neuronal caliber. They may also play a role in intracellular transport to axons and dendrites. This gene encodes the light chain neurofilament protein. Mutations in this gene cause Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease types 1F (CMT1F) and 2E (CMT2E), disorders of the peripheral nervous system that are characterized by distinct neuropathies. A pseudogene has been identified on chromosome Y. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2008],
- Function:
- caution:The sequence shown here is derived from an Ensembl automatic analysis pipeline and should be considered as preliminary data.,disease:Defects in NEFL are the cause of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1F (CMT1F) [MIM:607734]. CMT1F is a form of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, the most common inherited disorder of the peripheral nervous system. Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease is classified in two main groups on the basis of electrophysiologic properties and histopathology: primary peripheral demyelinating neuropathy or CMT1, and primary peripheral axonal neuropathy or CMT2. Neuropathies of the CMT1 group are characterized by severely reduced nerve conduction velocities (less than 38 m/sec), segmental demyelination and remyelination with onion bulb formations on nerve biopsy, slowly progressive distal muscle atrophy and weakness, absent deep tendon reflexes, and hollow feet. CMT1F is charac
- Subcellular Location:
- Cytoplasmic
- Expression:
- Cytoplasmic
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
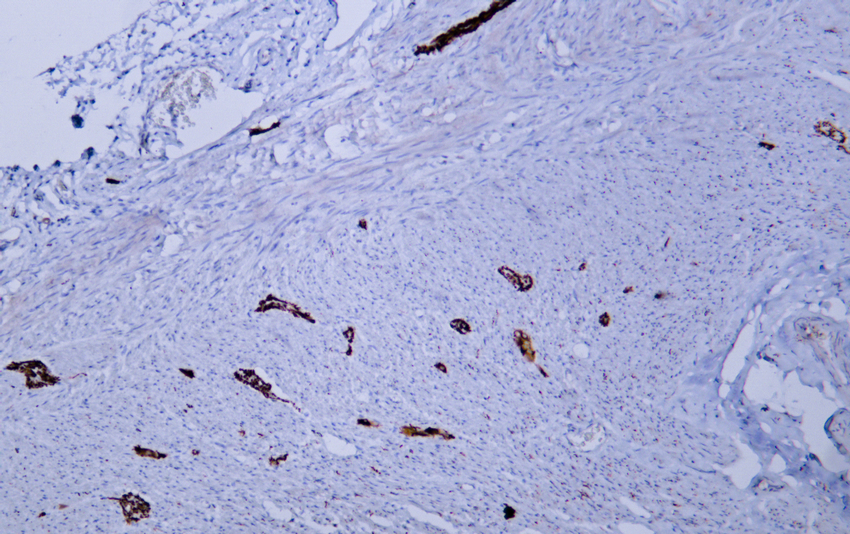
- Human appendix tissue was stained with Anti-Neurofilament (ABT456) Antibody
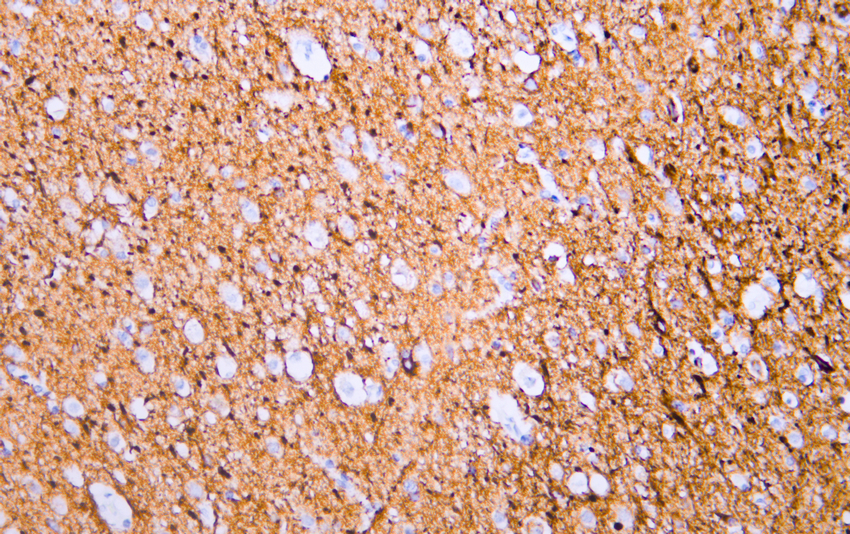
- Human cerebrum tissue was stained with Anti-Neurofilament (ABT456) Antibody
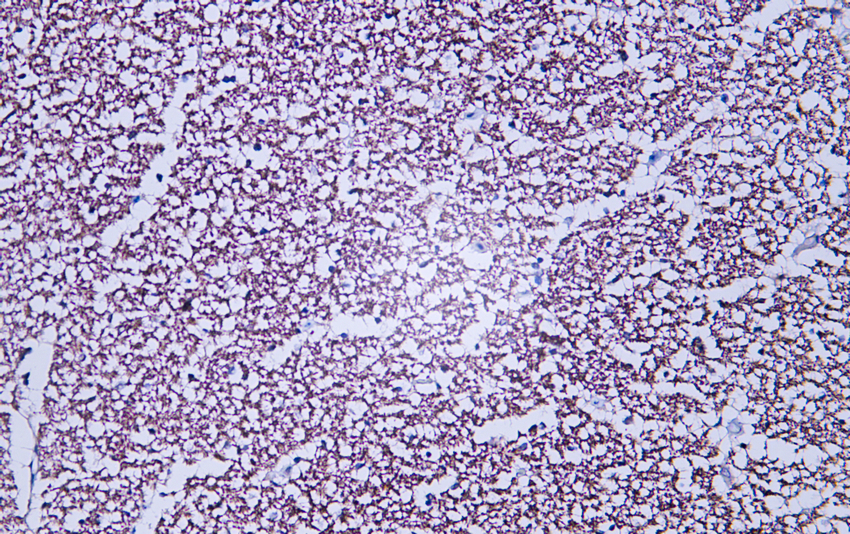
- Human hippocampus tissue was stained with Anti-Neurofilament (ABT456) Antibody
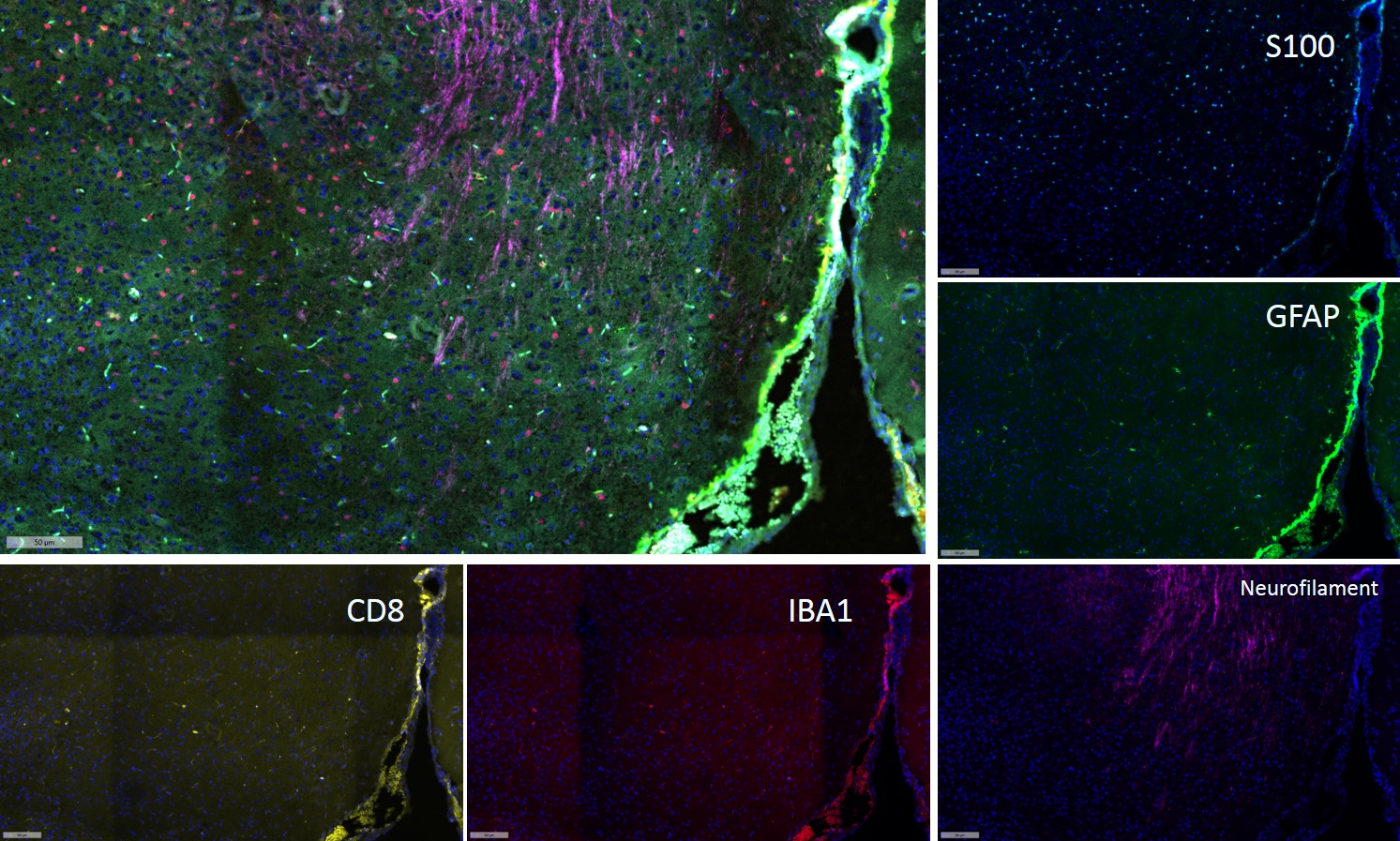
- Fluorescence multiplex immunohistochemical analysis of Mouse brain tissue (formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded section). The immunostaining was performed by Sextuple-Fluorescence kit (RS0039, Immunoway). GFAP mouse mAb(YM4426 Immunoway) green, S100 mouse mAb(YM6987 Immunoway) cyan,Neurofilament mouse mAb(YM6897 Immunoway) purple,Iba 1 mouse mAb(YM4765 Immunoway) red,CD8 a mouse mAb(YM4815 Immunoway) yellow, The section was incubated in 5 rounds of staining; sequentially for Anti-antibodies; each using a separate fluorescent tyramide signal amplification system. EDTA based antigen retrieval (Immunoway YS0004, pH 9.0, 20 minutes) was used in between rounds of tyramide signal amplification to remove the antibody from the previous round, to avoid any cross-reactivity. DAPI (dark blue) was used as a nuclear counter stain. Microscopy and pseudocoloring of individual dyes was performed using a Slideviewer Imaging System (Excilone).



