HNF4-α (phospho Ser313) Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YP0951
- Applications:WB;IHC;IF;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Target:
- HNF4α
- Fields:
- >>AMPK signaling pathway;>>Maturity onset diabetes of the young
- Gene Name:
- HNF4A
- Protein Name:
- Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4-alpha
- Human Gene Id:
- 3172
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P41235
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 15378
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P49698
- Rat Gene Id:
- 25735
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- P22449
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human HNF4 alpha around the phosphorylation site of Ser313. AA range:280-329
- Specificity:
- Phospho-HNF4-α (S313) Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of HNF4-α protein only when phosphorylated at S313.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. IHC 1:100 - 1:300. IF 1:200 - 1:1000. ELISA: 1:20000. Not yet tested in other applications.
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- HNF4A;HNF4;NR2A1;TCF14;Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4-alpha;HNF-4-alpha;Nuclear receptor subfamily 2 group A member 1;Transcription factor 14;TCF-14;Transcription factor HNF-4
- Observed Band(KD):
- 52kD
- Background:
- The protein encoded by this gene is a nuclear transcription factor which binds DNA as a homodimer. The encoded protein controls the expression of several genes, including hepatocyte nuclear factor 1 alpha, a transcription factor which regulates the expression of several hepatic genes. This gene may play a role in development of the liver, kidney, and intestines. Mutations in this gene have been associated with monogenic autosomal dominant non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus type I. Alternative splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants encoding several different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2012],
- Function:
- alternative products:Additional isoforms seem to exist,disease:Defects in HNF4A are the cause of maturity onset diabetes of the young type 1 (MODY1) [MIM:125850]; also shortened MODY-1. MODY [MIM:606391] is a form of diabetes that is characterized by an autosomal dominant mode of inheritance, onset in childhood or early adulthood (usually before 25 years of age) and a primary defect in insulin secretion. The clinical phenotype of MODY1 is characterized by severe insulin secretory defects, and by major hyperglycemia associated with microvascular complications.,function:Transcriptionally controlled transcription factor. Binds to DNA sites required for the transcription of alpha 1-antitrypsin, apolipoprotein CIII, transthyretin genes and HNF1-alpha. May be essential for development of the liver, kidney and intestine.,miscellaneous:Binds fatty acids.,online information:Hepatocyte nuclear fac
- Subcellular Location:
- Nucleus.
- Expression:
- Kidney,Liver,
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
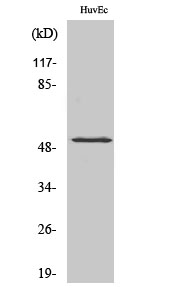
- Western Blot analysis of various cells using Phospho-HNF4-α (S313) Polyclonal Antibody diluted at 1:1000
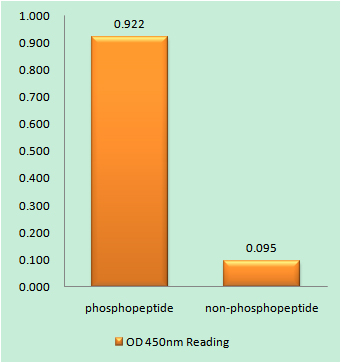
- Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (Phospho-ELISA) for Immunogen Phosphopeptide (Phospho-left) and Non-Phosphopeptide (Phospho-right), using HNF4 alpha (Phospho-Ser313) Antibody
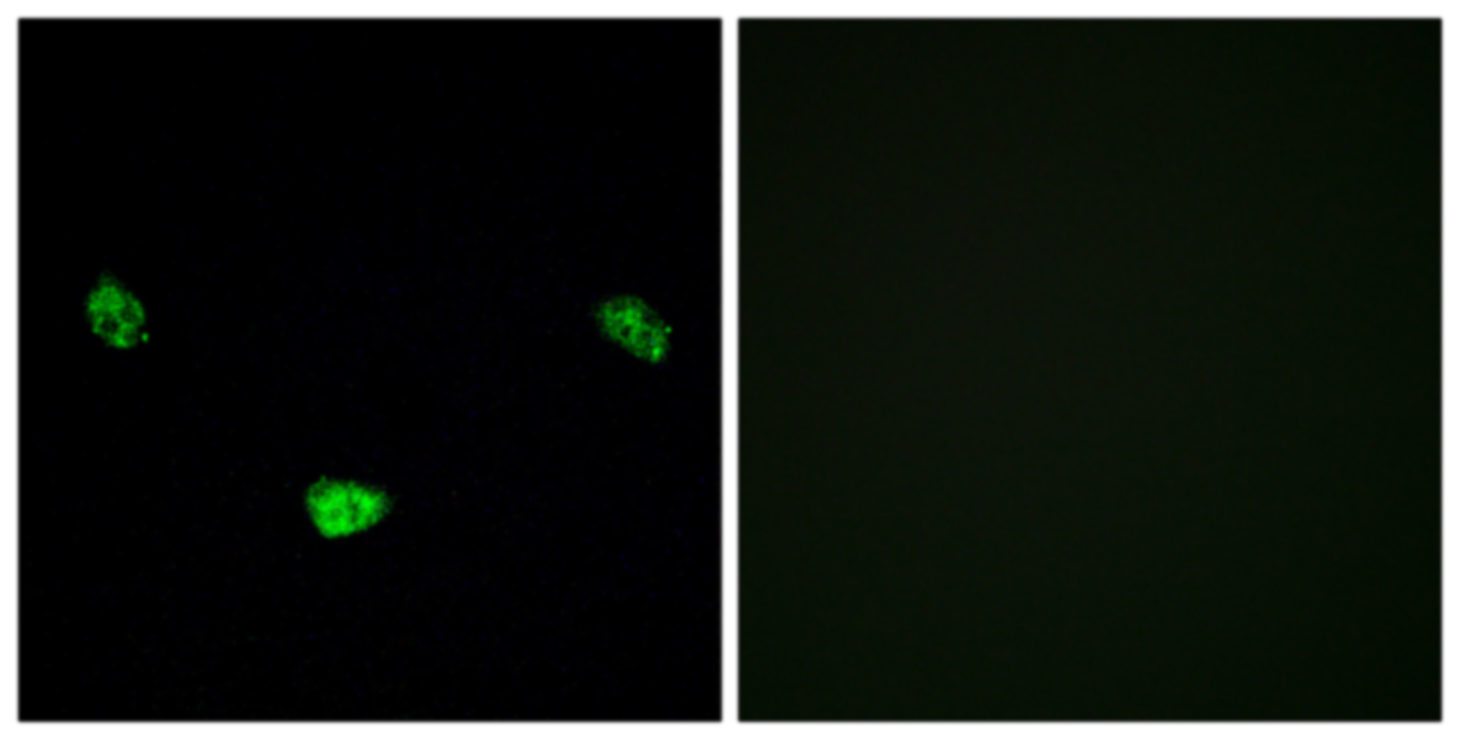
- Immunofluorescence analysis of LOVO cells, using HNF4 alpha (Phospho-Ser313) Antibody. The picture on the right is blocked with the phospho peptide.

- Immunohistochemistry analysis of paraffin-embedded human liver carcinoma, using HNF4 alpha (Phospho-Ser313) Antibody. The picture on the right is blocked with the phospho peptide.
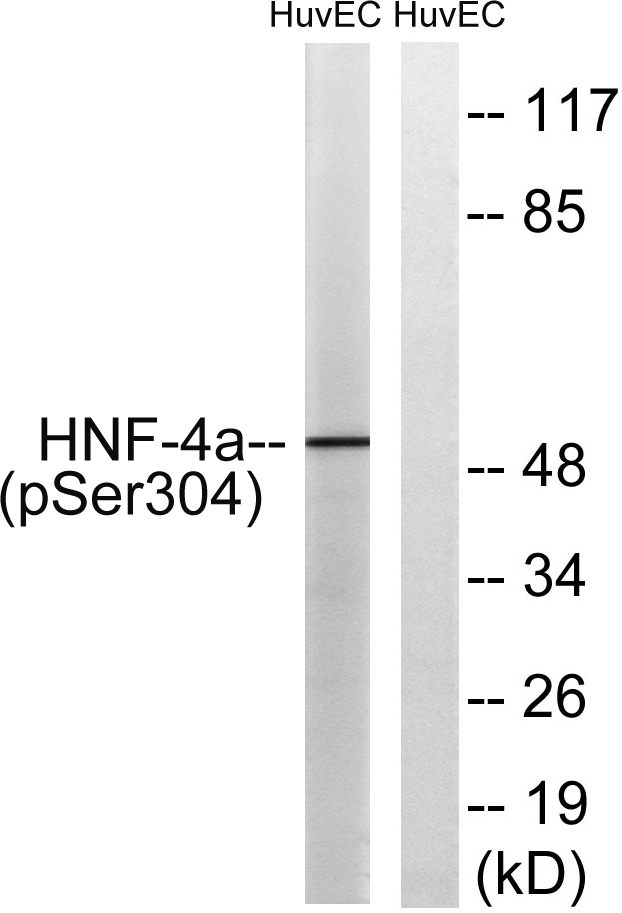
- Western blot analysis of lysates from HUVEC cells treated with EGF 200ng/ml 30', using HNF4 alpha (Phospho-Ser313) Antibody. The lane on the right is blocked with the phospho peptide.



