AQP2 (phospho Ser256) Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YP0978
- Applications:IHC;IF;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Target:
- AQP2
- Fields:
- >>Vasopressin-regulated water reabsorption
- Gene Name:
- AQP2
- Protein Name:
- Aquaporin-2
- Human Gene Id:
- 359
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P41181
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 11827
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P56402
- Rat Gene Id:
- 25386
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- P34080
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human Aquaporin 2 around the phosphorylation site of Ser256. AA range:222-271
- Specificity:
- Phospho-AQP2 (S256) Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of AQP2 protein only when phosphorylated at S256.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- IHC 1:100 - 1:300. ELISA: 1:40000.. IF 1:50-200
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- AQP2;Aquaporin-2;AQP-2;ADH water channel;Aquaporin-CD;AQP-CD;Collecting duct water channel protein;WCH-CD;Water channel protein for renal collecting duct
- Molecular Weight(Da):
- 29kD
- Background:
- This gene encodes a water channel protein located in the kidney collecting tubule. It belongs to the MIP/aquaporin family, some members of which are clustered together on chromosome 12q13. Mutations in this gene have been linked to autosomal dominant and recessive forms of nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2008],
- Function:
- disease:Defects in AQP2 are the cause of diabetes insipidus nephrogenic autosomal (ANDI) [MIM:125800]; also known as diabetes insipidus nephrogenic type 2. ANDI is caused by the inability of the renal collecting ducts to absorb water in response to arginine vasopressin. It is characterized by excessive water drinking (polydypsia), excessive urine excretion (polyuria), persistent hypotonic urine, and hypokalemia. Inheritance can be autosomal dominant or recessive.,domain:Aquaporins contain two tandem repeats each containing three membrane-spanning domains and a pore-forming loop with the signature motif Asn-Pro-Ala (NPA).,function:Forms a water-specific channel that provides the plasma membranes of renal collecting duct with high permeability to water, thereby permitting water to move in the direction of an osmotic gradient.,online information:AQP2 pages,PTM:Ser-256 phosphorylation is nec
- Subcellular Location:
- Apical cell membrane ; Multi-pass membrane protein . Basolateral cell membrane ; Multi-pass membrane protein . Cell membrane ; Multi-pass membrane protein . Cytoplasmic vesicle membrane ; Multi-pass membrane protein . Golgi apparatus, trans-Golgi network membrane ; Multi-pass membrane protein . Shuttles from vesicles to the apical membrane (PubMed:15509592). Vasopressin-regulated phosphorylation is required for translocation to the apical cell membrane (PubMed:15509592). PLEKHA8/FAPP2 is required to transport AQP2 from the TGN to sites where AQP2 is phosphorylated (By similarity). .
- Expression:
- Expressed in collecting tubules in kidney medulla (at protein level) (PubMed:7510718). Detected in kidney (PubMed:7510718).
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
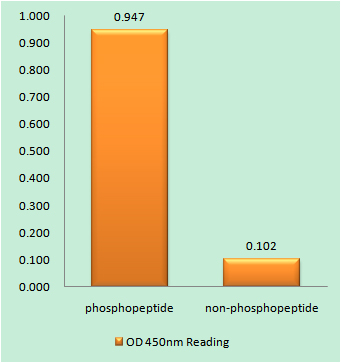
- Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (Phospho-ELISA) for Immunogen Phosphopeptide (Phospho-left) and Non-Phosphopeptide (Phospho-right), using Aquaporin 2 (Phospho-Ser256) Antibody
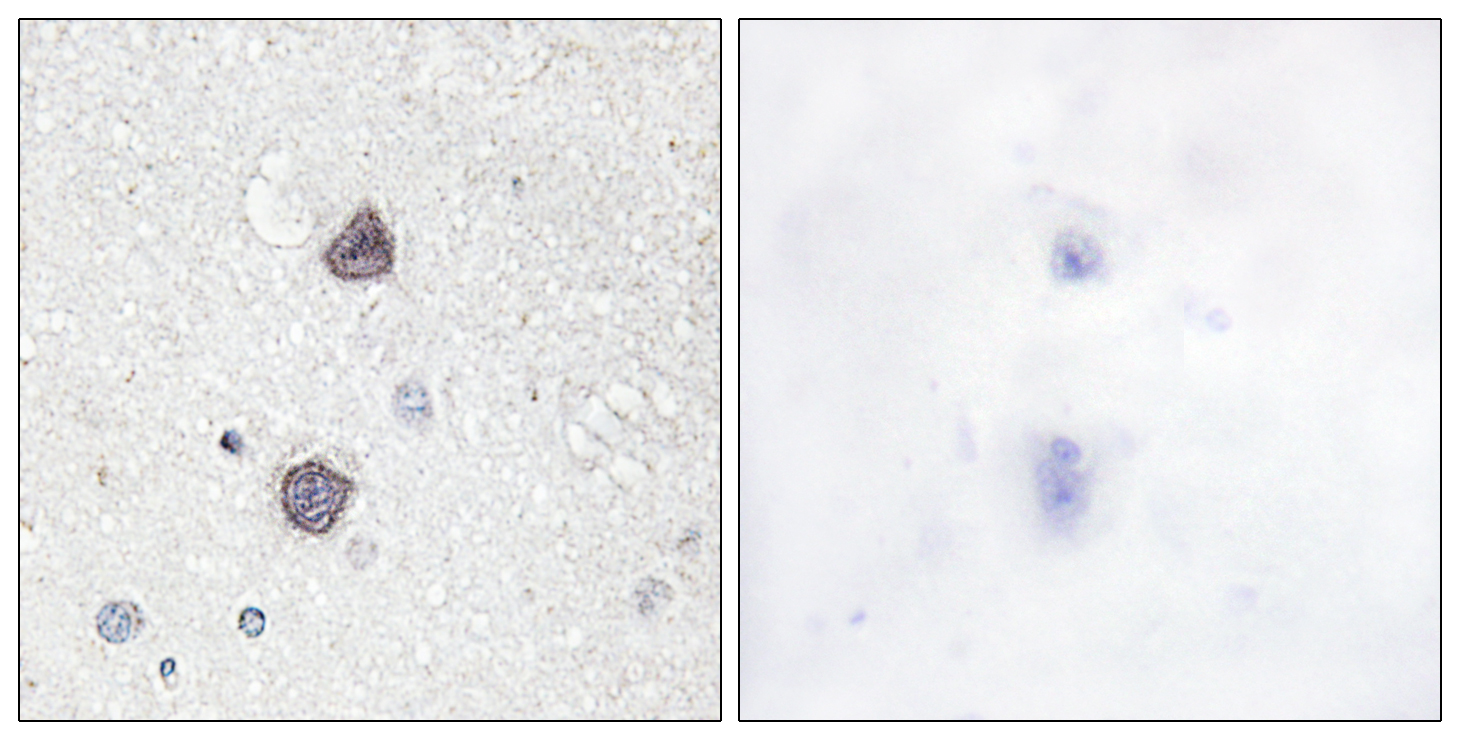
- Immunohistochemistry analysis of paraffin-embedded human brain, using Aquaporin 2 (Phospho-Ser256) Antibody. The picture on the right is blocked with the phospho peptide.



