KCNQ2/3/4/5 (phospho Thr217/246/223/251) Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YP1006
- Applications:WB;IHC;IF;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Target:
- KCNQ2/3/4/5
- Fields:
- >>Cholinergic synapse
- Gene Name:
- KCNQ2
- Protein Name:
- Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily KQT member 2
- Human Gene Id:
- 3785/3786/9132/56479
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- O43526/O43525/P56696/Q9NR82
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 16536/110862/60613/226922
- Rat Gene Id:
- 170848/29682
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- O88943/O88944/Q9JK96
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human Kv7.3/KCNQ3 around the phosphorylation site of Thr246. AA range:191-240
- Specificity:
- Phospho-KCNQ2/3/4/5 (T217/246/223/251) Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of KCNQ2/3/4/5 protein only when phosphorylated at T217/246/223/251.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500-2000 IHC 1:100 - 1:300. ELISA: 1:20000. IF 1:50-200
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- KCNQ2;Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily KQT member 2;KQT-like 2;Neuroblastoma-specific potassium channel subunit alpha KvLQT2;Voltage-gated potassium channel subunit Kv7.2;KCNQ3;Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily KQT me
- Molecular Weight(Da):
- 97kD
- Background:
- The M channel is a slowly activating and deactivating potassium channel that plays a critical role in the regulation of neuronal excitability. The M channel is formed by the association of the protein encoded by this gene and a related protein encoded by the KCNQ3 gene, both integral membrane proteins. M channel currents are inhibited by M1 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors and activated by retigabine, a novel anti-convulsant drug. Defects in this gene are a cause of benign familial neonatal convulsions type 1 (BFNC), also known as epilepsy, benign neonatal type 1 (EBN1). At least five transcript variants encoding five different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],
- Function:
- alternative products:Additional isoforms seem to exist,disease:Defects in KCNQ2 are the cause of benign neonatal epilepsy type 1 (EBN1) [MIM:121200]. Benign neonatal epilepsy is characterized by clusters of seizures occurring in the first days of life. Most patients have spontaneous remission by 12 months of age and show normal psychomotor development. The disorder is distinguished from benign familial infantile seizures by an earlier age at onset.,disease:Defects in KCNQ2 are the cause of benign neonatal epilepsy with myokymia (EBNMK) [MIM:606437]. EBNMK is a syndrome characterized by benign neonatal convulsions followed later in life by myokymia.,disease:Defects in KCNQ2 are the cause of myokymia isolated type 2 (MK2) [MIM:606437]. Myokymia is a condition characterized by spontaneous involuntary contraction of muscle fiber groups that can be observed as vermiform movement of the overly
- Subcellular Location:
- Cell membrane ; Multi-pass membrane protein .
- Expression:
- In adult and fetal brain. Highly expressed in areas containing neuronal cell bodies, low in spinal cord and corpus callosum. Isoform 2 is preferentially expressed in differentiated neurons. Isoform 6 is prominent in fetal brain, undifferentiated neuroblastoma cells and brain tumors.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
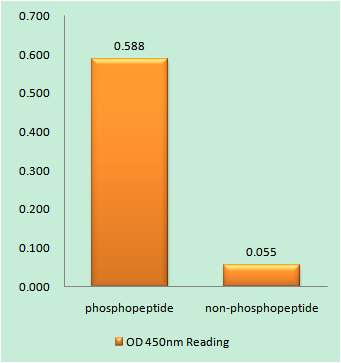
- Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (Phospho-ELISA) for Immunogen Phosphopeptide (Phospho-left) and Non-Phosphopeptide (Phospho-right), using Kv7.3/KCNQ3 (Phospho-Thr246) Antibody
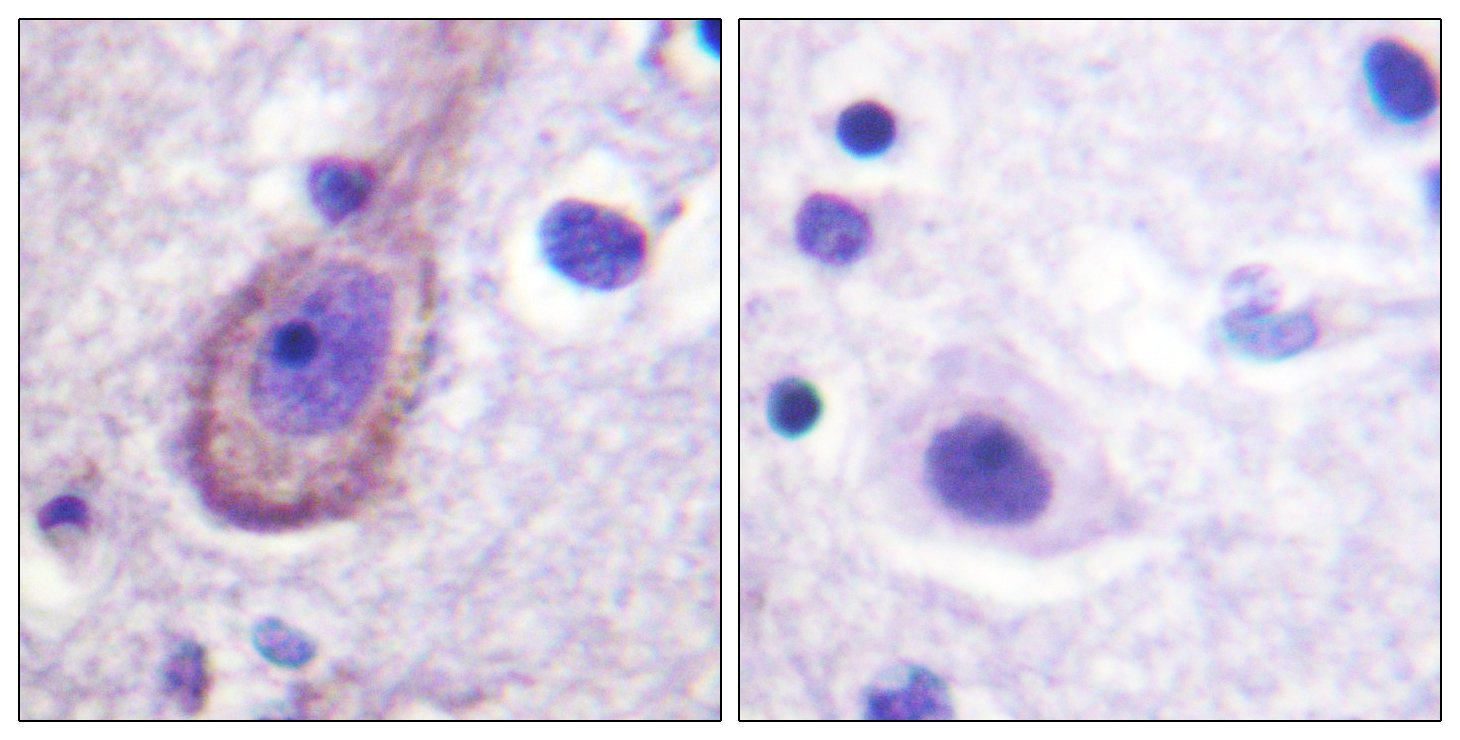
- Immunohistochemistry analysis of paraffin-embedded human brain, using Kv7.3/KCNQ3 (Phospho-Thr246) Antibody. The picture on the right is blocked with the phospho peptide.



