ATP5I Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YT0407
- Applications:WB;IHC;IF;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Rat;Mouse;
- Target:
- ATP5I
- Fields:
- >>Oxidative phosphorylation;>>Metabolic pathways;>>Thermogenesis
- Gene Name:
- ATP5I
- Protein Name:
- ATP synthase subunit e mitochondrial
- Human Gene Id:
- 521
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P56385
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- Q06185
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human ATP5I. AA range:20-69
- Specificity:
- ATP5I Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of ATP5I protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. IHC 1:100 - 1:300. ELISA: 1:20000.. IF 1:50-200
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- ATP5I;ATP5K;ATP synthase subunit e; mitochondrial;ATPase subunit e
- Observed Band(KD):
- 8kD
- Background:
- Mitochondrial ATP synthase catalyzes ATP synthesis, utilizing an electrochemical gradient of protons across the inner membrane during oxidative phosphorylation. It is composed of two linked multi-subunit complexes: the soluble catalytic core, F1, and the membrane-spanning component, Fo, which comprises the proton channel. The F1 complex consists of 5 different subunits (alpha, beta, gamma, delta, and epsilon) assembled in a ratio of 3 alpha, 3 beta, and a single representative of the other 3. The Fo seems to have nine subunits (a, b, c, d, e, f, g, F6 and 8). This gene encodes the e subunit of the Fo complex. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants.[provided by RefSeq, Jun 2010],
- Function:
- function:Mitochondrial membrane ATP synthase (F(1)F(0) ATP synthase or Complex V) produces ATP from ADP in the presence of a proton gradient across the membrane which is generated by electron transport complexes of the respiratory chain. F-type ATPases consist of two structural domains, F(1) - containing the extramembraneous catalytic core, and F(0) - containing the membrane proton channel, linked together by a central stalk and a peripheral stalk. During catalysis, ATP synthesis in the catalytic domain of F(1) is coupled via a rotary mechanism of the central stalk subunits to proton translocation. Part of the complex F(0) domain. Minor subunit located with subunit a in the membrane.,similarity:Belongs to the ATPase e subunit family.,subunit:F-type ATPases have 2 components, CF(1) - the catalytic core - and CF(0) - the membrane proton channel. CF(0) seems to have nine subunits: a, b, c,
- Subcellular Location:
- Mitochondrion. Mitochondrion inner membrane.
- Expression:
- Fetal brain,Kidney,
Exosomal connexin 43 regulates the resistance of glioma cells to temozolomide. ONCOLOGY REPORTS Oncol Rep. 2021 Apr;45(4):1-10 WB Human 1:1000 U251r cell
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images

- Immunofluorescence analysis of Siha cell. 1,primary Antibody was diluted at 1:100(4°C overnight). 2, Goat Anti Rabbit IgG (H&L) - AFluor 594 Secondary antibody(catalog No: RS3611) was diluted at 1:500(room temperature, 50min).

- Western Blot analysis of various cells using ATP5I Polyclonal Antibody
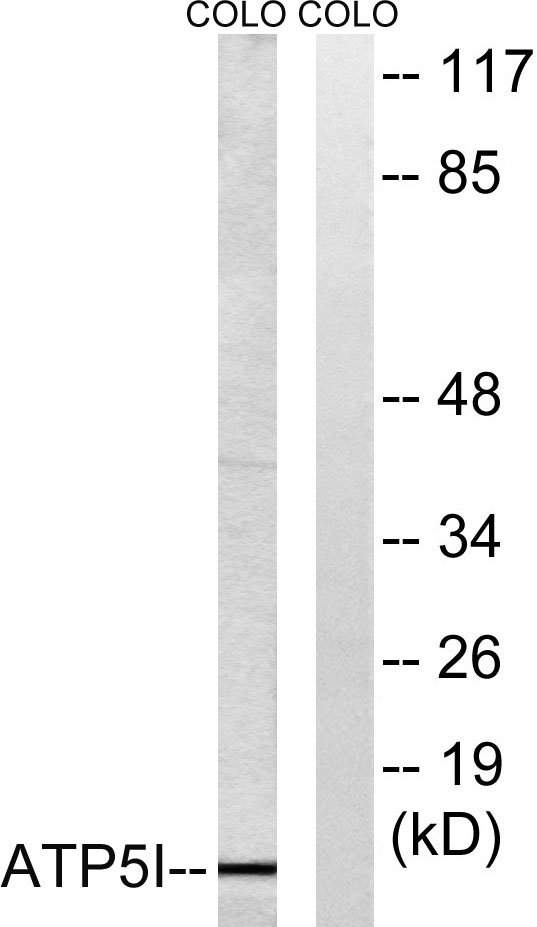
- Western blot analysis of lysates from COLO cells, using ATP5I Antibody. The lane on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.
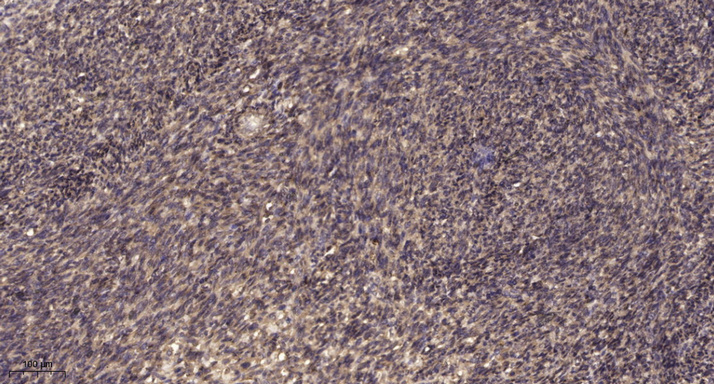
- Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human uterus. 1, Antibody was diluted at 1:200(4° overnight). 2, Tris-EDTA,pH9.0 was used for antigen retrieval. 3,Secondary antibody was diluted at 1:200(room temperature, 45min).



