Connexin-26 Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YT1050
- Applications:WB;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Target:
- Connexin-26
- Gene Name:
- GJB2
- Protein Name:
- Gap junction beta-2 protein
- Human Gene Id:
- 2706
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P29033
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 14619
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- Q00977
- Rat Gene Id:
- 394266
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- P21994
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human Connexin-26. AA range:45-94
- Specificity:
- Connexin-26 Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of Connexin-26 protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. ELISA: 1:5000. Not yet tested in other applications.
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- GJB2;Gap junction beta-2 protein;Connexin-26;Cx26
- Observed Band(KD):
- 26kD
- Background:
- This gene encodes a member of the gap junction protein family. The gap junctions were first characterized by electron microscopy as regionally specialized structures on plasma membranes of contacting adherent cells. These structures were shown to consist of cell-to-cell channels that facilitate the transfer of ions and small molecules between cells. The gap junction proteins, also known as connexins, purified from fractions of enriched gap junctions from different tissues differ. According to sequence similarities at the nucleotide and amino acid levels, the gap junction proteins are divided into two categories, alpha and beta. Mutations in this gene are responsible for as much as 50% of pre-lingual, recessive deafness. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2008],
- Function:
- disease:Defects in GJB2 are a cause of keratitis-ichthyosis-deafness syndrome (KID syndrome) [MIM:148210]; an autosomal dominant form of ectodermal dysplasia. Ectodermal dysplasias (EDs) constitute a heterogeneous group of developmental disorders affecting tissues of ectodermal origin. EDs are characterized by abnormal development of two or more ectodermal structures such as hair, teeth, nails and sweat glands, with or without any additional clinical sign. Each combination of clinical features represents a different type of ectodermal dysplasia. KID syndrome is characterized by the association of hyperkeratotic skin lesions with vascularizing keratitis and profound sensorineural hearing loss. Clinical features include deafness, ichthyosis, photobia, absent or decreased eyebrows, sparse or absent scalp hair, decreased sweating and dysplastic finger and toenails.,disease:Defects in GJB2 ar
- Subcellular Location:
- Cell membrane ; Multi-pass membrane protein . Cell junction, gap junction . Colocalizes with GJB4 at gap junction plaques in the cochlea. .
- Expression:
- Blood,Colon,
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
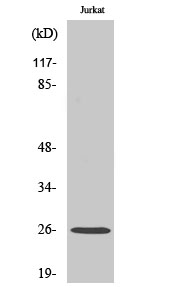
- Western Blot analysis of various cells using Connexin-26 Polyclonal Antibody diluted at 1:500

- Western blot analysis of lysate from Jurkat cells, using Connexin-26 antibody.



