MSH2 Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YT2896
- Applications:IHC;IF;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Target:
- MSH2
- Fields:
- >>Platinum drug resistance;>>Mismatch repair;>>Pathways in cancer;>>Colorectal cancer
- Gene Name:
- MSH2
- Protein Name:
- DNA mismatch repair protein Msh2
- Human Gene Id:
- 4436
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P43246
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 17685
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P43247
- Rat Gene Id:
- 81709
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- P54275
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human MSH2. AA range:541-590
- Specificity:
- MSH2 Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of MSH2 protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- IHC 1:100 - 1:300. IF 1:200 - 1:1000. ELISA: 1:20000. Not yet tested in other applications.
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- MSH2;DNA mismatch repair protein Msh2;hMSH2;MutS protein homolog 2
- Observed Band(KD):
- 100kD
- Background:
- This locus is frequently mutated in hereditary nonpolyposis colon cancer (HNPCC). When cloned, it was discovered to be a human homolog of the E. coli mismatch repair gene mutS, consistent with the characteristic alterations in microsatellite sequences (RER+ phenotype) found in HNPCC. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2012],
- Function:
- disease:Defects in MSH2 are a cause of Muir-Torre syndrome (MTS) [MIM:158320]. MTS is a rare autosomal dominant disorder characterized by sebaceous neoplasms and visceral malignancy.,disease:Defects in MSH2 are a cause of susceptibility to endometrial cancer [MIM:608089].,disease:Defects in MSH2 are the cause of hereditary non-polyposis colorectal cancer type 1 (HNPCC1) [MIM:120435]. Mutations in more than one gene locus can be involved alone or in combination in the production of the HNPCC phenotype (also called Lynch syndrome). Most families with clinically recognized HNPCC have mutations in either MLH1 or MSH2 genes. HNPCC is an autosomal, dominantly inherited disease associated with marked increase in cancer susceptibility. It is characterized by a familial predisposition to early onset colorectal carcinoma (CRC) and extra-colonic cancers of the gastrointestinal, urological and femal
- Subcellular Location:
- Nucleus . Chromosome .
- Expression:
- Ubiquitously expressed.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
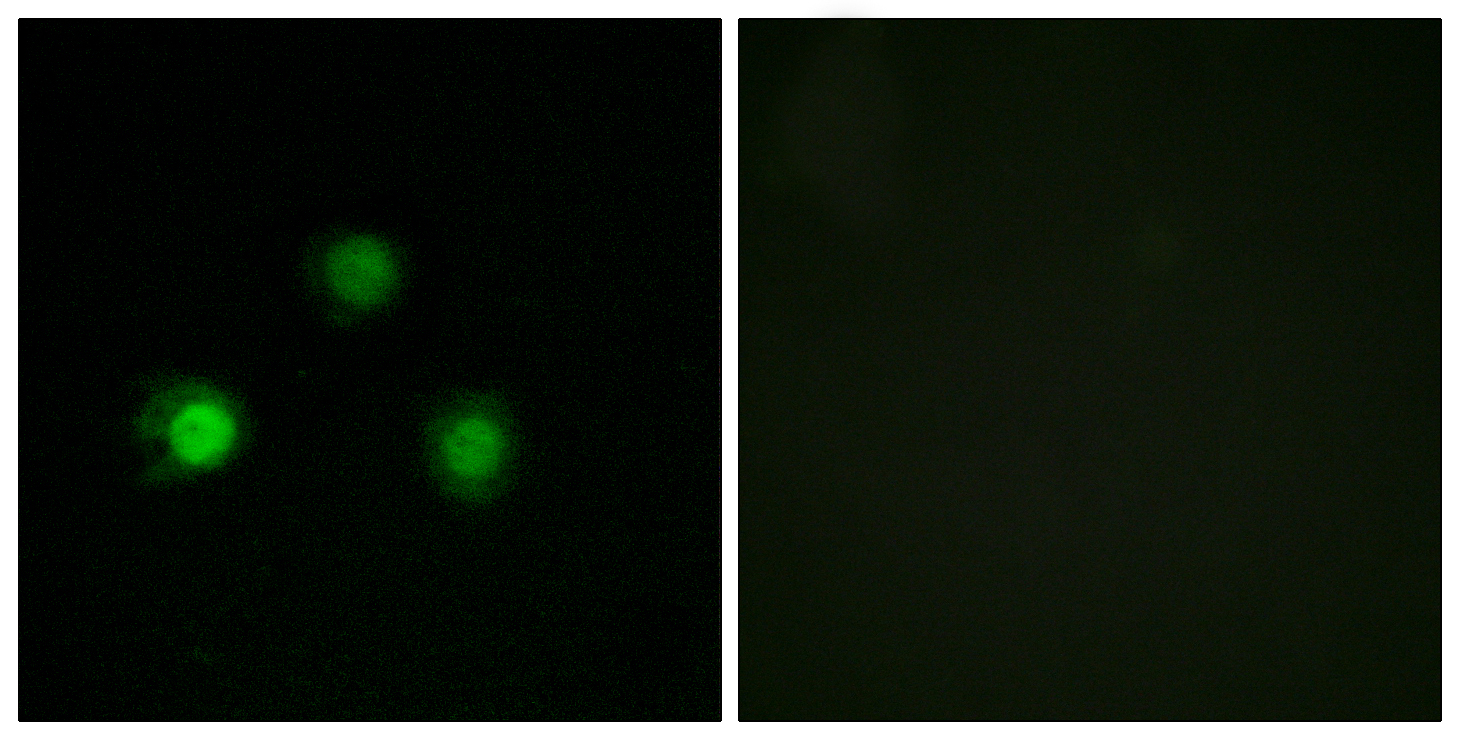
- Immunofluorescence analysis of HUVEC cells, using MSH2 Antibody. The picture on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.
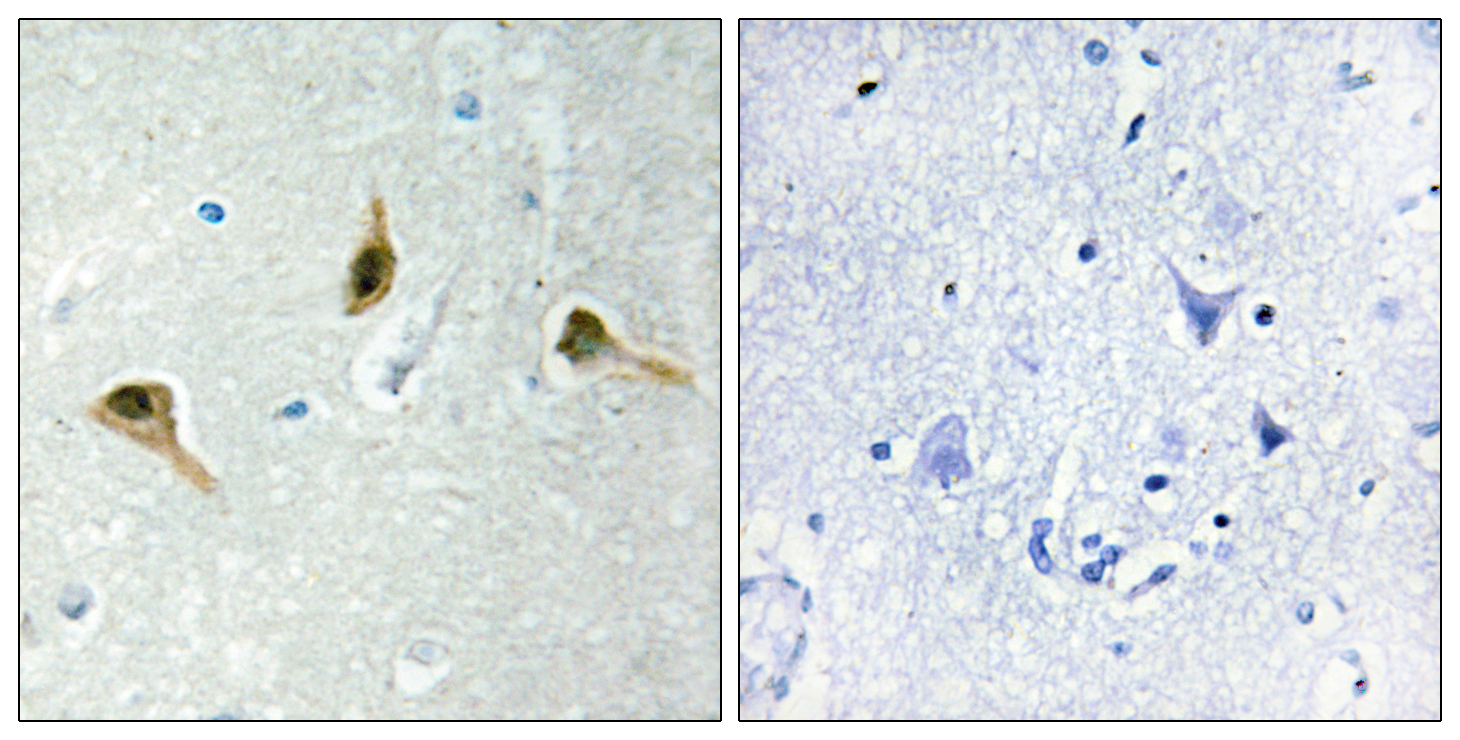
- Immunohistochemistry analysis of paraffin-embedded human brain tissue, using MSH2 Antibody. The picture on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.



