NCX1 Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YT5103
- Applications:WB;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Target:
- NCX1
- Fields:
- >>Calcium signaling pathway;>>cGMP-PKG signaling pathway;>>Cardiac muscle contraction;>>Adrenergic signaling in cardiomyocytes;>>Apelin signaling pathway;>>Olfactory transduction;>>Endocrine and other factor-regulated calcium reabsorption;>>Protein digestion and absorption;>>Mineral absorption;>>Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy;>>Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy;>>Dilated cardiomyopathy
- Gene Name:
- SLC8A1
- Protein Name:
- Sodium/calcium exchanger 1
- Human Gene Id:
- 6546
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P32418
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 20541
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P70414
- Rat Gene Id:
- 29715
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- Q01728
- Immunogen:
- Synthesized peptide derived from NCX1 . at AA range: 270-350
- Specificity:
- NCX1 Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of NCX1 protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. ELISA: 1:5000. Not yet tested in other applications.
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- SLC8A1;CNC;NCX1;Sodium/calcium exchanger 1;Na(+)/Ca(2+)-exchange protein 1
- Observed Band(KD):
- 108kD
- Background:
- In cardiac myocytes, Ca(2+) concentrations alternate between high levels during contraction and low levels during relaxation. The increase in Ca(2+) concentration during contraction is primarily due to release of Ca(2+) from intracellular stores. However, some Ca(2+) also enters the cell through the sarcolemma (plasma membrane). During relaxation, Ca(2+) is sequestered within the intracellular stores. To prevent overloading of intracellular stores, the Ca(2+) that entered across the sarcolemma must be extruded from the cell. The Na(+)-Ca(2+) exchanger is the primary mechanism by which the Ca(2+) is extruded from the cell during relaxation. In the heart, the exchanger may play a key role in digitalis action. The exchanger is the dominant mechanism in returning the cardiac myocyte to its resting state following excitation.[supplied by OMIM, Apr 2004],
- Function:
- alternative products:Additional isoforms seem to exist,enzyme regulation:By ATP.,function:Rapidly transports Ca(2+) during excitation-contraction coupling. Ca(2+) is extruded from the cell during relaxation so as to prevent overloading of intracellular stores.,similarity:Belongs to the sodium/potassium/calcium exchanger family. SLC8 subfamily.,similarity:Contains 2 Calx-beta domains.,tissue specificity:Cardiac sarcolemma.,
- Subcellular Location:
- Cell membrane ; Multi-pass membrane protein .
- Expression:
- Detected primarily in heart and at lower levels in brain (PubMed:1374913). Expressed in cardiac sarcolemma, brain, kidney, liver, pancreas, skeletal muscle, placenta and lung (PubMed:1476165).
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
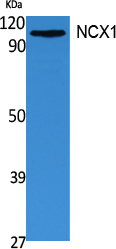
- Western Blot analysis of extracts from 293 cells, using NCX1 Polyclonal Antibody. Secondary antibody(catalog#:RS0002) was diluted at 1:20000



