Protein C Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YT5221
- Applications:WB;IHC;IF;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Rat;Mouse;
- Target:
- Protein C
- Fields:
- >>Complement and coagulation cascades
- Gene Name:
- PROC
- Protein Name:
- Vitamin K-dependent protein C
- Human Gene Id:
- 5624
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P04070
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P33587
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from the Internal region of human PROC. AA range:181-230
- Specificity:
- Protein C Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of Protein C protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. IHC: 1:100-300 ELISA: 1:20000.. IF 1:50-200
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- PROC;Vitamin K-dependent protein C;Anticoagulant protein C;Autoprothrombin IIA;Blood coagulation factor XIV
- Observed Band(KD):
- 52kD
- Background:
- This gene encodes a vitamin K-dependent plasma glycoprotein. The encoded protein is cleaved to its activated form by the thrombin-thrombomodulin complex. This activated form contains a serine protease domain and functions in degradation of the activated forms of coagulation factors V and VIII. Mutations in this gene have been associated with thrombophilia due to protein C deficiency, neonatal purpura fulminans, and recurrent venous thrombosis.[provided by RefSeq, Dec 2009],
- Function:
- catalytic activity:Degradation of blood coagulation factors Va and VIIIa.,disease:Defects in PROC are the cause of protein C deficiency autosomal dominant (ADPROCD) [MIM:176860]. ADPROCD is a cause of hereditary thrombophilia, a hemostatic disorder characterized by impaired regulation of blood coagulation and a tendency to recurrent venous thrombosis. However, many adults with heterozygous disease may be asymptomatic. Individuals with decreased amounts of protein C are classically referred to as having type I protein C deficiency and those with normal amounts of a functionally defective protein as having type II deficiency.,disease:Defects in PROC are the cause of protein C deficiency autosomal recessive (ARPROCD) [MIM:612304]. ARPROCD results in a thrombotic condition that can manifest as a severe neonatal disorder or as a milder disorder with late-onset thrombophilia. The severe form l
- Subcellular Location:
- Secreted . Golgi apparatus . Endoplasmic reticulum .
- Expression:
- Plasma; synthesized in the liver.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
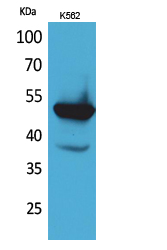
- Western Blot analysis of K562 cells using Protein C Polyclonal Antibody. Secondary antibody(catalog#:RS0002) was diluted at 1:20000
.jpg)
- Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human-colon, antibody was diluted at 1:100
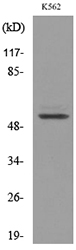
- Western blot analysis of lysate from K562 cells, using PROC Antibody.



