NFATc1 Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YT5381
- Applications:WB;IHC;IF;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse
- Target:
- NFATc1
- Fields:
- >>MAPK signaling pathway;>>cGMP-PKG signaling pathway;>>cAMP signaling pathway;>>Cellular senescence;>>Wnt signaling pathway;>>Osteoclast differentiation;>>C-type lectin receptor signaling pathway;>>Natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity;>>Th1 and Th2 cell differentiation;>>Th17 cell differentiation;>>T cell receptor signaling pathway;>>B cell receptor signaling pathway;>>Oxytocin signaling pathway;>>AGE-RAGE signaling pathway in diabetic complications;>>Yersinia infection;>>Hepatitis B;>>Human cytomegalovirus infection;>>Human T-cell leukemia virus 1 infection;>>Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus infection;>>Human immunodeficiency virus 1 infection;>>PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer;>>Inflammatory bowel disease;>>Lipid and atherosclerosis
- Gene Name:
- NFATC1
- Protein Name:
- Nuclear factor of activated T-cells cytoplasmic 1
- Human Gene Id:
- 4772
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- O95644
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- O88942
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from the C-terminal region of human NFATC1. AA range:881-930
- Specificity:
- NFATc1 Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of NFATc1 protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500-2000;IHC 1:100-500;IF ICC 1:100-500;ELISA 1:5000-20000
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- NFATC1;NFAT2;NFATC;Nuclear factor of activated T-cells, cytoplasmic 1;NF-ATc1;NFATc1;NFAT transcription complex cytosolic component;NF-ATc;NFATc
- Observed Band(KD):
- 105kD
- Background:
- The product of this gene is a component of the nuclear factor of activated T cells DNA-binding transcription complex. This complex consists of at least two components: a preexisting cytosolic component that translocates to the nucleus upon T cell receptor (TCR) stimulation, and an inducible nuclear component. Proteins belonging to this family of transcription factors play a central role in inducible gene transcription during immune response. The product of this gene is an inducible nuclear component. It functions as a major molecular target for the immunosuppressive drugs such as cyclosporin A. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been identified for this gene. Different isoforms of this protein may regulate inducible expression of different cytokine genes. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2013],
- Function:
- alternative products:Isoform C-alpha and isoform C-beta are the strongest activator of gene transcription, followed by isoform A-alpha and isoform A-beta, whereas isoform B-alpha and isoform B-beta are the weakest. Isoform B-alpha, isoform B-beta, isoform C-alpha and isoform C-beta, both present in T-cells, can modulate their transcriptional activity,domain:Isoforms C have a C-terminal part with an additional trans-activation domain, TAD-B, which acts as a transcriptional activator. Isoforms B have a shorter C-terminal part without complete TAD-B which acts as a transcriptional repressor.,domain:Rel Similarity Domain (RSD) allows DNA-binding and cooperative interactions with AP1 factors.,domain:The N-terminal transactivation domain (TAD-A) binds to and is activated by Cbp/p300. The dephosphorylated form contains two unmasked nuclear localization signals (NLS), which allow translocation o
- Subcellular Location:
- Cytoplasm . Nucleus . Cytoplasmic for the phosphorylated form and nuclear after activation that is controlled by calcineurin-mediated dephosphorylation. Rapid nuclear exit of NFATC is thought to be one mechanism by which cells distinguish between sustained and transient calcium signals. The subcellular localization of NFATC plays a key role in the regulation of gene transcription (PubMed:16511445). Nuclear translocation of NFATC1 is enhanced in the presence of TNFSF11. Nuclear translocation is decreased in the presence of FBN1 which can bind and sequester TNFSF11 (By similarity). .
- Expression:
- Expressed in thymus, peripheral leukocytes as T-cells and spleen. Isoforms A are preferentially expressed in effector T-cells (thymus and peripheral leukocytes) whereas isoforms B and isoforms C are preferentially expressed in naive T-cells (spleen). Isoforms B are expressed in naive T-cells after first antigen exposure and isoforms A are expressed in effector T-cells after second antigen exposure. Isoforms IA are widely expressed but not detected in liver nor pancreas, neural expression is strongest in corpus callosum. Isoforms IB are expressed mostly in muscle, cerebellum, placenta and thymus, neural expression in fetal and adult brain, strongest in corpus callosum.
NCX1 disturbs calcium homeostasis and promotes RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation by regulating JNK/c-Fos/NFATc1 signaling pathway in multiple myeloma
PD0325901, an ERK inhibitor, attenuates RANKL‐induced osteoclast formation and mitigates cartilage inflammation by inhibiting the NF-κB and MAPK pathways BIOORGANIC CHEMISTRY Ting Jiang, Yuhang Gong, Wekang Zhang, Jianxin Qiu, Xiaohang Zheng, Ze Li, Guangyong Yang, Zhenghua Hong WB Mouse BMMs
Effect of Enterococcus faecalis on osteoclastogenesis under cobalt-mimicked hypoxia in vitro MICROBIAL PATHOGENESIS Fengyi Zhou, Xin Li, Xiaochi Chang, Zhihao Geng, Wenjing Hao, Jing Deng, Hai Ming Wong, Shuai Wang WB Mouse BMMs
The transcription factor Prox1 is essential for satellite cell differentiation and muscle fibre-type regulation. Nature Communications 2016 Oct 12 WB,IF Human 1:1000,1:100 C2C12 cell
AZ-628 delays osteoarthritis progression via inhibiting the TNF-α-induced chondrocyte necroptosis and regulating osteoclast formation INTERNATIONAL IMMUNOPHARMACOLOGY Shuang Mi WB,IF Mouse
Paroxetine Attenuates Chondrocyte Pyroptosis and Inhibits Osteoclast Formation by Inhibiting NF-κB Pathway Activation to Delay Osteoarthritis Progression. Drug Design Development and Therapy Huaxing Hong WB Mouse 1:1000 bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMMs)
EPSTI1 promotes osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption by PKR/NF-κB signaling BIOCHEMICAL AND BIOPHYSICAL RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS Muzi Zhang WB Mouse 1:1000 RAW264.7 cell
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images

- Western Blot analysis of HuvEc cells using NFATc1 Polyclonal Antibody. Secondary antibody(catalog#:RS0002) was diluted at 1:20000
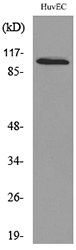
- Western blot analysis of lysate from HUVEC cells, using NFATC1 Antibody.
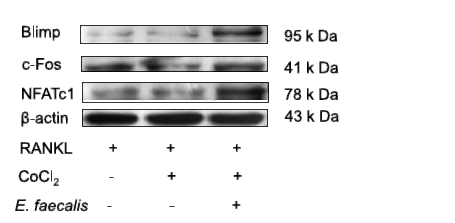
- Effect of Enterococcus faecalis on osteoclastogenesis under cobalt-mimicked hypoxia in vitro MICROBIAL PATHOGENESIS Fengyi Zhou, Xin Li, Xiaochi Chang, Zhihao Geng, Wenjing Hao, Jing Deng, Hai Ming Wong, Shuai Wang WB Mouse BMMs



