CD267 Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YT5632
- Applications:WB;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse
- Target:
- CD267
- Fields:
- >>Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction;>>Intestinal immune network for IgA production;>>Primary immunodeficiency
- Gene Name:
- TNFRSF13B
- Protein Name:
- Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 13B
- Human Gene Id:
- 23495
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- O14836
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 57916
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- Q9ET35
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from the Internal region of human TNFRSF13B. AA range:81-130
- Specificity:
- CD267 Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of CD267 protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. ELISA: 1:10000. Not yet tested in other applications.
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- TNFRSF13B;TACI;Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 13B;Transmembrane activator and CAML interactor;CD267
- Observed Band(KD):
- 32kD
- Background:
- The protein encoded by this gene is a lymphocyte-specific member of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor superfamily. It interacts with calcium-modulator and cyclophilin ligand (CAML). The protein induces activation of the transcription factors NFAT, AP1, and NF-kappa-B and plays a crucial role in humoral immunity by interacting with a TNF ligand. This gene is located within the Smith-Magenis syndrome region on chromosome 17. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],
- Function:
- disease:Defects in TNFRSF13B are a cause of common variable immunodeficiency (CVID) [MIM:240500]. CVID is characterized by a deficiency in all immunoglobulin (Ig) isotypes. Individuals with CVID suffer from recurrent sinopulmonary and gastrointestinal infections and have an increased incidence of autoimmune disorders and of lymphoid and non-lymphoid malignancies. There is evidence for a global isotype switching defect in some individuals with CVID. But CVID is a complex and heterogeneous disease in which defects in B-cell survival, number of circulating CD27+ memory B-cells (including IgM+CD27+ B-cells), B-cell activation after antigen receptor cross-linking, T-cell signaling and cytokine expression have been observed.,disease:Defects in TNFRSF13B are a cause of immunoglobulin A deficiency 2 (IGAD2) [MIM:609529]. Selective deficiency of immunoglobulin A (IGAD) is the most common form of
- Subcellular Location:
- Membrane; Single-pass type III membrane protein.
- Expression:
- Highly expressed in spleen, thymus, small intestine and peripheral blood leukocytes. Expressed in resting B-cells and activated T-cells, but not in resting T-cells.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
- Western Blot analysis of NIH-3T3 cells using CD267 Polyclonal Antibody. Secondary antibody(catalog#:RS0002) was diluted at 1:20000
.jpg)
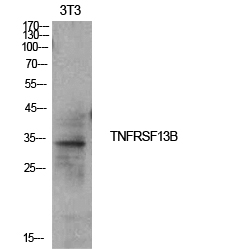
- Western Blot analysis of 3T3 cells using CD267 Polyclonal Antibody. Secondary antibody(catalog#:RS0002) was diluted at 1:20000



