EDA Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YT5703
- Applications:WB;IHC;IF;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse
- Target:
- EDA
- Fields:
- >>Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction;>>NF-kappa B signaling pathway
- Gene Name:
- EDA
- Protein Name:
- Ectodysplasin-A
- Human Gene Id:
- 1896
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- Q92838
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 13607
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- O54693
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from the Internal region of human EDA. AA range:120-170
- Specificity:
- EDA Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of EDA protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. IHC: 1:100-1:300. ELISA: 1:10000.. IF 1:50-200
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- EDA;ED1;EDA2;Ectodysplasin-A;Ectodermal dysplasia protein;EDA protein
- Observed Band(KD):
- 42kD
- Background:
- The protein encoded by this gene is a type II membrane protein that can be cleaved by furin to produce a secreted form. The encoded protein, which belongs to the tumor necrosis factor family, acts as a homotrimer and may be involved in cell-cell signaling during the development of ectodermal organs. Defects in this gene are a cause of ectodermal dysplasia, anhidrotic, which is also known as X-linked hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia. Several transcript variants encoding many different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],
- Function:
- alternative products:Additional isoforms seem to exist,disease:Defects in EDA are a cause of hypodontia [MIM:300606]. Hypodontia is agenesis of two or more permanent teeth without associated systemic disorders. Hypodontia due to EDA defects is an X-linked recessive disorder. Affected individuals have normal hair, skin, and nails, but lack primary and permanent teeth.,disease:Defects in EDA are the cause of ectodermal dysplasia, type 1 (ED1) [MIM:305100]; also known as Christ-Siemens-Touraine syndrome or X-linked hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia (XLHED). Ectodermal dysplasia defines a heterogeneous group of disorders due to abnormal development of two or more ectodermal structures. ED1 is a disease characterized by sparse hair (atrichosis or hypotrichosis), abnormal or missing teeth and the inability to sweat due to the absence of sweat glands. ED1 is the most common form of over 150 cli
- Subcellular Location:
- Cell membrane ; Single-pass type II membrane protein .; [Ectodysplasin-A, secreted form]: Secreted .
- Expression:
- Not abundant; expressed in specific cell types of ectodermal (but not mesodermal) origin of keratinocytes, hair follicles, sweat glands. Also in adult heart, liver, muscle, pancreas, prostate, fetal liver, uterus, small intestine and umbilical chord.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
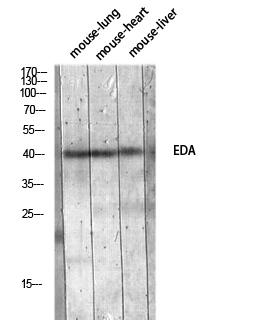
- Western blot analysis of mouse-lung mouse-heart mouse-liver lysis using EDA antibody. Antibody was diluted at 1:1000. Secondary antibody(catalog#:RS0002) was diluted at 1:20000
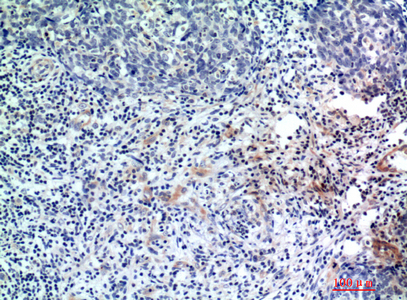
- Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human-breast-cancer, antibody was diluted at 1:200



