Flt-4 Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YT5878
- Applications:WB;IHC;IF;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Target:
- VEGFR3
- Fields:
- >>MAPK signaling pathway;>>Ras signaling pathway;>>Rap1 signaling pathway;>>Calcium signaling pathway;>>PI3K-Akt signaling pathway;>>Focal adhesion;>>Pathways in cancer;>>Breast cancer
- Gene Name:
- FLT4 VEGFR3
- Protein Name:
- Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 (VEGFR-3) (EC 2.7.10.1) (Fms-like tyrosine kinase 4) (FLT-4) (Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor FLT4)
- Human Gene Id:
- 2324
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P35916
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 14257
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P35917
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- Q91ZT1
- Immunogen:
- Synthetic peptide from human protein at AA range: 640-700
- Specificity:
- The antibody detects endogenous Flt-4
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500-2000,IHC 1:500-200, ELISA 1:10000-20000. IF 1:50-200
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 (VEGFR-3;EC 2.7.10.1;Fms-like tyrosine kinase 4;FLT-4;Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor FLT4)
- Observed Band(KD):
- 170kD
- Background:
- This gene encodes a tyrosine kinase receptor for vascular endothelial growth factors C and D. The protein is thought to be involved in lymphangiogenesis and maintenance of the lymphatic endothelium. Mutations in this gene cause hereditary lymphedema type IA. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],
- Function:
- catalytic activity:ATP + a [protein]-L-tyrosine = ADP + a [protein]-L-tyrosine phosphate.,disease:Defects in FLT4 are found in juvenile hemangioma. Juvenile hemangiomas are the most common tumors of infancy, occurring as many as 10% of all births. These benign vascular lesions enlarge rapidly during the first year of life by hyperplasia of endothelial cells and attendant pericytes, and then spontaneously involute over a period of years, leaving loose fibrofatty tissue.,disease:Defects in FLT4 are the cause of lymphedema hereditary type 1 (LYH1A) [MIM:153100]; also known as Nonne-Milroy lymphedema or Milroy disease. Hereditary lymphedema is a chronic disabling condition which results in swelling of the extremities due to altered lymphatic flow. Patients with lymphedema suffer from recurrent local infections and physical impairment.,function:Receptor for VEGFC. Has a tyrosine-protein kinas
- Subcellular Location:
- Cell membrane ; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Cytoplasm . Nucleus . Ligand-mediated autophosphorylation leads to rapid internalization. .; [Isoform 1]: Cell membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Ligand-mediated autophosphorylation leads to rapid internalization.; [Isoform 2]: Cell membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein.; [Isoform 3]: Secreted. Cytoplasm.
- Expression:
- Detected in endothelial cells (at protein level). Widely expressed. Detected in fetal spleen, lung and brain. Detected in adult liver, muscle, thymus, placenta, lung, testis, ovary, prostate, heart, and kidney.
Eplerenone inhibits UUO-induced lymphangiogenesis and cardiac fibrosis by attenuating inflammatory injury. INTERNATIONAL IMMUNOPHARMACOLOGYInt Immunopharmacol. 2022 Jul;108:108759. Rat 1:100,1:100 heart tissues
Exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells regulate lymphangiogenesis via the miR-302d-3p/VEGFR3/AKT axis to ameliorate inflammatory bowel disease INTERNATIONAL IMMUNOPHARMACOLOGY Wei Qiu WB,IF Mouse
Eplerenone reduces lymphangiogenesis in the contralateral kidneys of UUO rats Scientific Reports Hao Juan IHC,WB Rat,Mouse kidney tissue
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
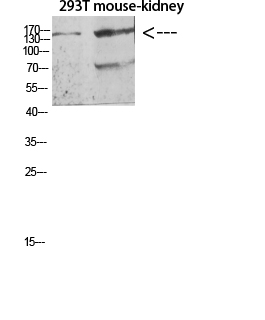
- Western blot analysis of K562 3T3 lysate, antibody was diluted at 500. Secondary antibody(catalog#:RS0002) was diluted at 1:20000
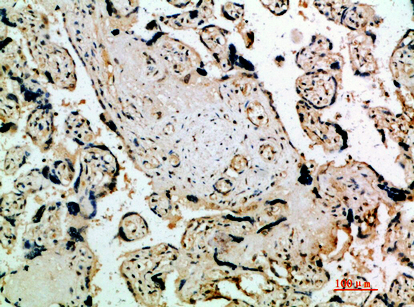
- Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human-placenta, antibody was diluted at 1:200



