Endoglin Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YT5879
- Applications:WB;IHC;IF;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse
- Target:
- CD105(Endoglin)
- Gene Name:
- ENG END
- Protein Name:
- Endoglin (CD antigen CD105)
- Human Gene Id:
- 2022
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P17813
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 13805
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- Q63961
- Immunogen:
- Synthetic peptide from human protein at AA range: 370-430
- Specificity:
- The antibody detects endogenous Endoglin
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500-2000,IHC 1:500-200, ELISA 1:10000-20000. IF 1:50-200
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- Endoglin (CD antigen CD105)
- Observed Band(KD):
- 70kD
- Background:
- This gene encodes a homodimeric transmembrane protein which is a major glycoprotein of the vascular endothelium. This protein is a component of the transforming growth factor beta receptor complex and it binds to the beta1 and beta3 peptides with high affinity. Mutations in this gene cause hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia, also known as Osler-Rendu-Weber syndrome 1, an autosomal dominant multisystemic vascular dysplasia. This gene may also be involved in preeclampsia and several types of cancer. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, May 2013],
- Function:
- disease:Defects in ENG are the cause of hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia type 1 (HHT1) [MIM:187300, 108010]; also known as Osler-Rendu-Weber syndrome 1 (ORW1). HHT1 is an autosomal dominant multisystemic vascular dysplasia, characterized by recurrent epistaxis, muco-cutaneous telangiectases, gastro-intestinal hemorrhage, and pulmonary (PAVM), cerebral (CAVM) and hepatic arteriovenous malformations; all secondary manifestations of the underlying vascular dysplasia. Although the first symptom of HHT1 in children is generally nose bleed, there is an important clinical heterogeneity.,function:Major glycoprotein of vascular endothelium. May play a critical role in the binding of endothelial cells to integrins and/or other RGD receptors.,subunit:Homodimer that forms an heteromeric complex with the signaling receptors for transforming growth factor-beta: TGF-beta receptors I and/or II. It
- Subcellular Location:
- Cell membrane ; Single-pass type I membrane protein .
- Expression:
- Detected on umbilical veil endothelial cells (PubMed:10625079). Detected in placenta (at protein level) (PubMed:1692830). Detected on endothelial cells (PubMed:1692830).
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
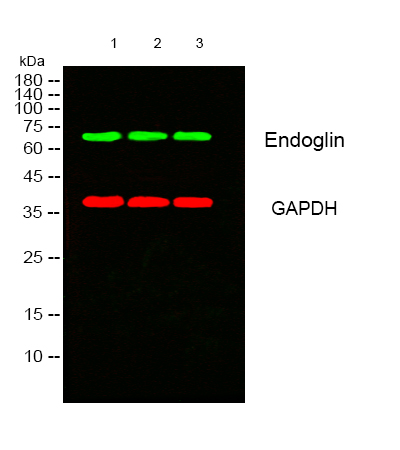

- Western blot analysis of lysates from 1) 3T3 , 2) K562 , 3) Hela cells, (Green) primary antibody was diluted at 1:1000, 4°over night, secondary antibody(cat:RS23920)was diluted at 1:10000, 37° 1hour. (Red) GAPDH Monoclonal Antibody(2B8) (cat:YM3029) antibody was diluted at 1:5000 as loading control, 4° over night,secondary antibody(cat:RS23710)was diluted at 1:10000, 37° 1hour.
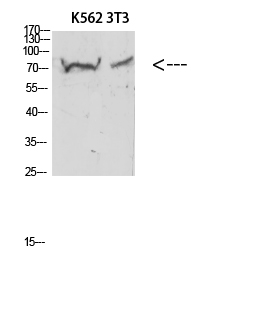
- Western blot analysis of 3T3 KB K562 Hela 293T lysate, antibody was diluted at 500. Secondary antibody(catalog#:RS0002) was diluted at 1:20000
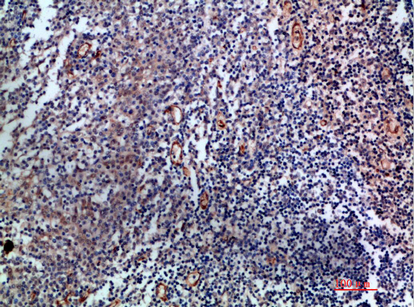
- Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human-tonsil, antibody was diluted at 1:200



