Rhodopsin (phospho Ser334) Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YP0966
- Applications:IHC;IF;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Target:
- Rhodopsin
- Fields:
- >>Phototransduction
- Gene Name:
- RHO
- Protein Name:
- Rhodopsin
- Human Gene Id:
- 6010
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P08100
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 212541
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P15409
- Rat Gene Id:
- 24717
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- P51489
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human Rhodopsin around the phosphorylation site of Ser334. AA range:299-348
- Specificity:
- Phospho-Rhodopsin (S334) Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of Rhodopsin protein only when phosphorylated at S334.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- IHC 1:100 - 1:300. ELISA: 1:10000.. IF 1:50-200
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- RHO;OPN2;Rhodopsin;Opsin-2
- Molecular Weight(Da):
- 39kD
- Background:
- Retinitis pigmentosa is an inherited progressive disease which is a major cause of blindness in western communities. It can be inherited as an autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive, or X-linked recessive disorder. In the autosomal dominant form,which comprises about 25% of total cases, approximately 30% of families have mutations in the gene encoding the rod photoreceptor-specific protein rhodopsin. This is the transmembrane protein which, when photoexcited, initiates the visual transduction cascade. Defects in this gene are also one of the causes of congenital stationary night blindness. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],
- Function:
- disease:Defects in RHO are a cause of retinitis pigmentosa autosomal recessive (ARRP) [MIM:268000].,disease:Defects in RHO are the cause of congenital stationary night blindness autosomal dominant type 1 (CSNBAD1) [MIM:610445]; also known as rhodopsin-related congenital stationary night blindness. Congenital stationary night blindness is a non-progressive retinal disorder characterized by impaired night vision.,disease:Defects in RHO are the cause of retinitis pigmentosa type 4 (RP4) [MIM:180380]. RP leads to degeneration of retinal photoreceptor cells. Patients typically have night vision blindness and loss of midperipheral visual field. As their condition progresses, they lose their far peripheral visual field and eventually central vision as well. RP4 inheritance is autosomal dominant.,function:Photoreceptor required for image-forming vision at low light intensity. Required for photor
- Subcellular Location:
- Membrane ; Multi-pass membrane protein . Cell projection, cilium, photoreceptor outer segment . Synthesized in the inner segment (IS) of rod photoreceptor cells before vectorial transport to disk membranes in the rod outer segment (OS) photosensory cilia. .
- Expression:
- Rod shaped photoreceptor cells which mediate vision in dim light.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
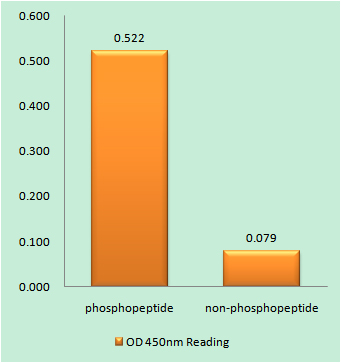
- Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (Phospho-ELISA) for Immunogen Phosphopeptide (Phospho-left) and Non-Phosphopeptide (Phospho-right), using Rhodopsin (Phospho-Ser334) Antibody
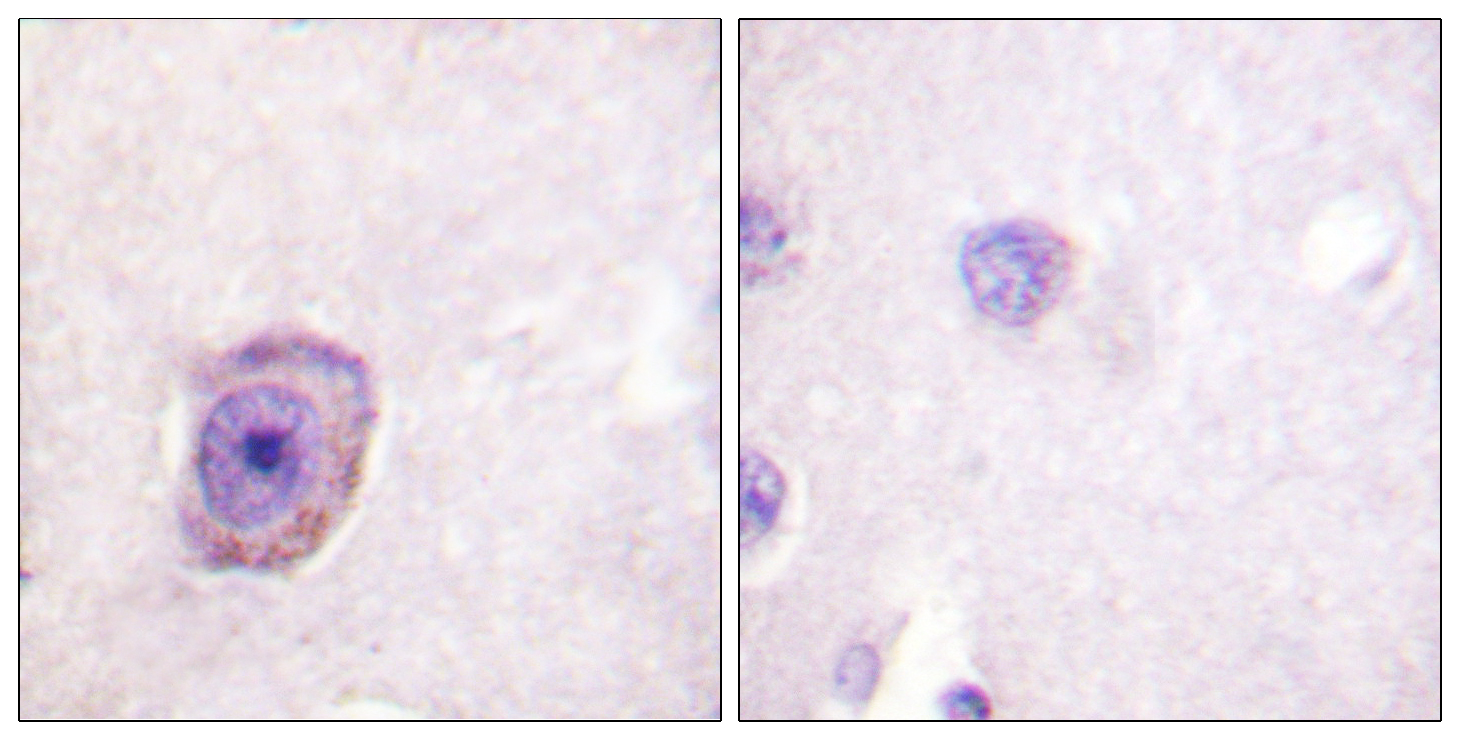
- Immunohistochemistry analysis of paraffin-embedded human brain, using Rhodopsin (Phospho-Ser334) Antibody. The picture on the right is blocked with the phospho peptide.

